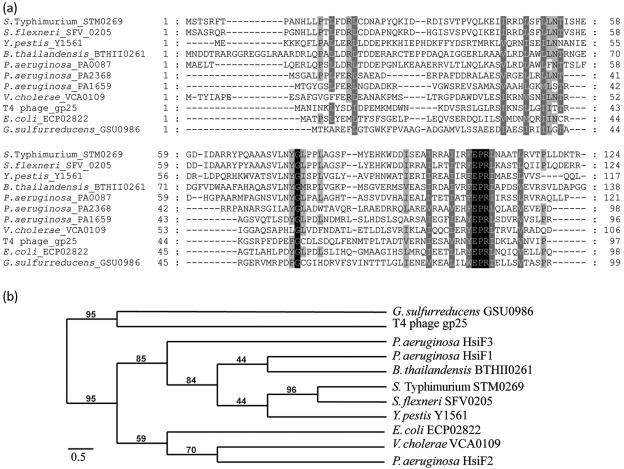
Fig. 1.
Amino acid sequence comparison and phylogenetic relationship among members of the gp25 family. (a) Identification of conserved residues in members of the gp25-like protein family. Amino acid sequence alignments of HsiF proteins of P. aeruginosa (HsiF1/PA0087, HsiF2/PA1659 and HsiF3/PA2368), T4 phage gp25, G. sulfurreducens GSU0986 and HsiF homologues found in other Gram-negative bacteria associated with a T6SS gene cluster (clustal w2, GeneDoc). Different levels of shading indicate the level of conservation (100 %, black; >80 %, dark grey; >60 %, light grey; <60 %, white). The amino acid position is indicated at the beginning and the end of each line. (b) Phylogenetic analysis of gp25-like proteins. Neighbour-joining tree based on HsiF proteins, gp25 of the T4 bacteriophage, GSU0986 of G. sulfurreducens and several HsiF orthologues found in Gram-negative bacteria that are associated with T6SS gene clusters. Indicated bootstrap values correspond to 100 replicates. Phylogenetic analysis was carried out using http://www.phylogeny.fr.