Figure 4.
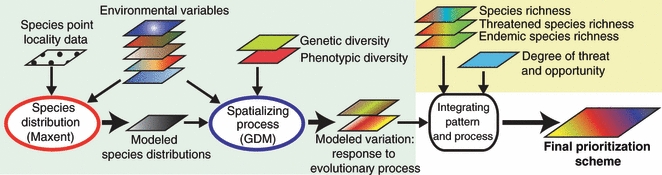
Proposed framework for integrating evolutionary processes (blue box) with traditionally used information on biodiversity patterns, levels of threat, and socio-economic information (yellow box) in conservation planning. Predictive models for spatializing species distributions and environmentally associated genetic and phenotypic variation are at the core of the approach. Modeled species distributions are used to delimit the study area for subsequent modeling of intra-specific variation, and can also provide the basis for the assessment of species richness. Environmental variables are used in modeling both species distributions and intra-specific variation, and could include remotely sensed data (e.g. tree cover, elevation, or moisture levels) and ground-based data (e.g. temperature and precipitation variables). Small arrows represent input, large arrows output.
