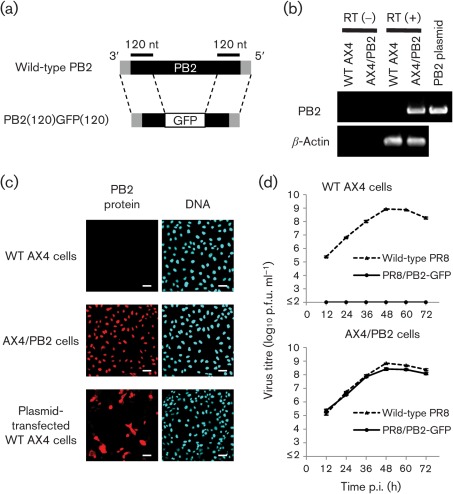
Fig. 1.
Characterization of PR8/PB2–GFP virus. (a) Schematic diagram of wild-type PB2 and PB2(120)GFP(120) vRNAs. PB2(120)GFP(120) vRNA possesses the 3′ non-coding region, 120 nt of the coding sequence of PB2 vRNA, the GFP gene and 120 nt of the 3′ and 5′ non-coding regions of PB2 vRNA. The non-coding region and coding regions of PB2 vRNA are represented by shaded and filled bars, respectively. (b) PB2 gene expression in AX4/PB2 cells. RNA was extracted from wild-type AX4 and AX4/PB2 cells. RT-PCR was performed using an oligo(dT) primer followed by cDNA synthesis and PCR with PB2-specific or canine β-actin-specific primers. (c) PB2 protein expression in AX4/PB2 cells. Cells were reacted with anti-PB2 antibody (clone 18/1; left panels) and the nuclei stained with Hoechst 33342 (right panels). Bars, 50 µm. (d) Growth kinetics of PR8/PB2–GFP monitored over 72 h. Wild-type AX4 and AX4/PB2 cells were infected with wild-type PR8 or PR8/PB2–GFP virus at an m.o.i. of 0.001. Supernatants collected at the indicated time points were assayed for infectious virus in plaque assays in AX4/PB2 cells.