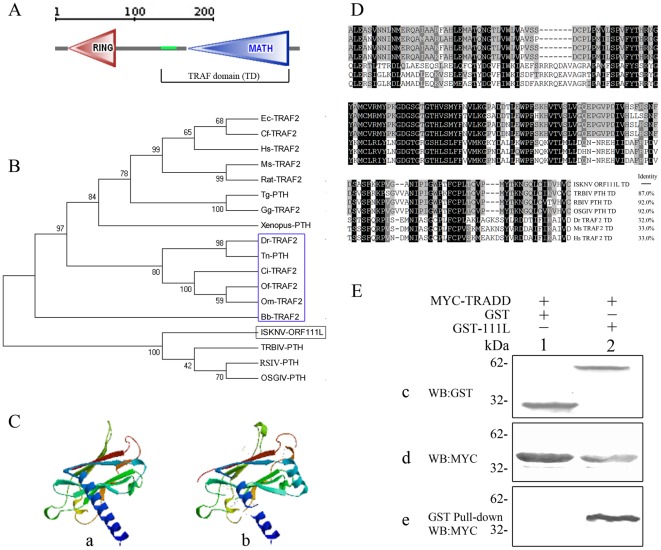
Figure 1. Bioinformatics analysis and protein interaction of ISKNV ORF111L.
(A) ISKNV ORF111L domain architecture was predicted by SMART program. (B) Phylogenetic tree of ISKNV ORF111L with other TRAF family proteins. The Bootstrap test of phylogeny was calculated 1000 replicates. The numbers at the nodes indicate bootstrap values. (C) Homology model structures analysis of TRAF domain from ISKNV ORF111L (panel a) and Homo sapiens (panel b). (D) Multiple sequence alignments of TRAF domain from different TRAF proteins. PTH, predicted TRAF homology; TD, TRAF domain. (E) Expression of GST proteins (c, lane 1), GST-111L fusion proteins (c, lane 2) and MYC-TRADD fusion proteins (d, lanes 1 and 2) were effective. After the GST pull down assay, MYC-TRADD fusion proteins were detected in the GST-111L sample (e, lane 2) but not in the GST control sample (e, lane 1), indicating the interaction between ISKNV ORF111L and zebrafish TRADD.