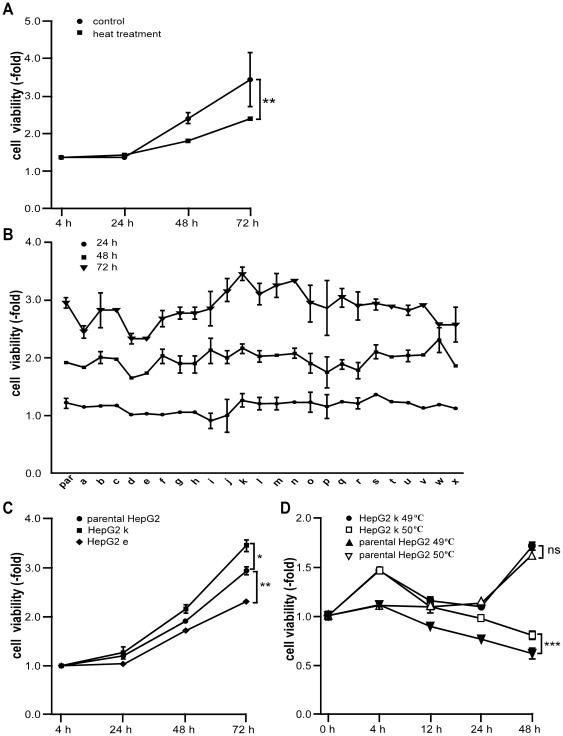
Figure 1. The viability of HepG2 cells and sublines derived from HepG2 cells after hyperthermia.
(A) HepG2 cells were cultured after 47°C heat treatment. The 24 h, 48 h and 72 h cell viability of HepG2 cells with or without 47°C heat treatment were measured using MTT assay. (B) Twenty-four sublines were established after 47°C heat treatment for 10 min as described in the method. The 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h viability was evaluated by MTT assay after 24 sublines were established. par, parental HepG2 cells; a–x, sublines derived from the HepG2 cells. (C) The 24 h, 48 h and 72 h viability of representative sublines of HepG2 cells were evaluated by MTT assay. (D) Parental HepG2 and HepG2 k cells were treated with 49°C or 50°C 10 min. The 4 h, 12 h, 24 h and 48 h cell viability were measured by MTT assay. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P <0.001. Data are the representative results of three independent experiments. The coefficients of variation (CV) of all assays were shown in Supporting Information S1.