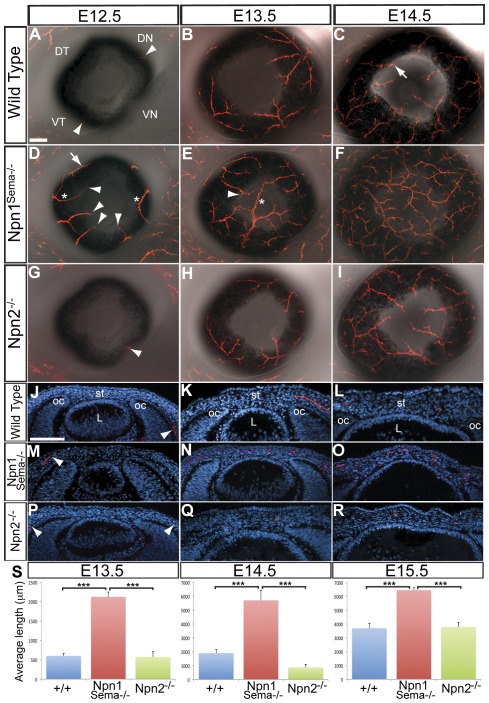
Figure 2. Innervation of the corneal stroma is defective in Npn1Sema−/− but normal in Npn2−/− mutant embryos.
Immunostaining for TuJ1 was performed on whole-mount corneas (A–I) and sections (J–R) at E12.5, E13.5 and E14.5. (A–C) Innervation of wild type cornea showing the spatiotemporal projection of nerve bundles into the four quadrants of the stroma and minimal contribution from the DT quadrant (arrow in C). (D) At E12.5, Npn1Sema−/− eyes show several aberrant projections (asterisks) that also innervate the DT quadrant (arrow) and extend close to the corneal periphery (black arrowheads). (E) By E13.5, nerve bundles from all quadrants including the DT quadrant (arrowhead) innervate the cornea and some project across the diameter of the cornea (asterisk). (F) At E14.5, extensively bifurcated nerve bundles cover most of the cornea. (G–I) Innervation of Npn2−/− eyes resembled wild type at these stages of corneal development. (J–R) Representative sections through wild type, Npn1Sema−/− and Npn2−/− mutant corneas showing the extent of nerve projections at each developmental stage. All sections were counterstained with DAPI. Arrowheads in J, M, and P show relative projection of nerve bundles in the periocular region at E12.5. (S) Quantification of nerves in wild type, Npn1Sema−/− and Npn2−/− mutant corneas was carried out by measuring the lengths of nerve bundles in the cornea at E13.5–E15.5; for details see Methods section. For all samples n = 8, except Npn2−/− mutants where n = 6 for E14.5 and E15.5. Error bars = SEM. Scale bars: 100 µm. ***, P<0.001.