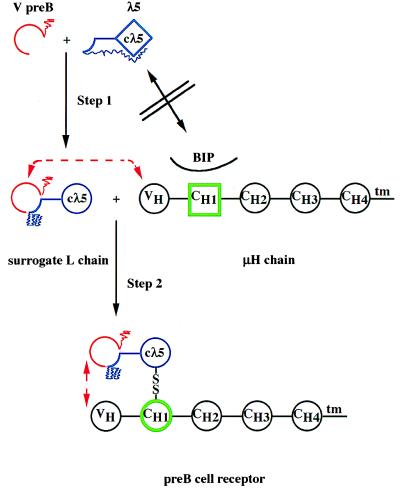
Figure 2.
Stepwise formation of the pre-B cell receptor.
Isolated λ5 protein has an improperly folded structure in
which Cλ5 (◊, blue) has not yet attained an Ig-domain
structure (○) and is associated with the amino terminal
unique portion of λ5, which acts as an intramolecular
chaperone ( ). The
β7 strand of the amino terminal λ5 portion
is folded in an Ig-domain- like fashion
(
). The
β7 strand of the amino terminal λ5 portion
is folded in an Ig-domain- like fashion
( ). The VpreB
protein is folded as an Ig-like domain, missing the
β7-strand with a unique, non-Ig carboxyl terminal portion
(
). The VpreB
protein is folded as an Ig-like domain, missing the
β7-strand with a unique, non-Ig carboxyl terminal portion
( , red). The isolated
λ5-protein cannot displace BIP and associate with the
CH1-domain of the μH chain, because neither
λ5 (◊) nor CH1 (□, green) are
properly Ig-domain-folded. Association of VpreB with
λ5 induces an Ig-domain-structure in Cλ5
and displaces the intramolecular chaperone
(
, red). The isolated
λ5-protein cannot displace BIP and associate with the
CH1-domain of the μH chain, because neither
λ5 (◊) nor CH1 (□, green) are
properly Ig-domain-folded. Association of VpreB with
λ5 induces an Ig-domain-structure in Cλ5
and displaces the intramolecular chaperone
( ). VpreB
interacts with VH of the μH chain, Cλ5
displaces BIP and induces an Ig-domain structure in CH1
(○, green), forms a disulfide bridge and thus, the pre-B
cell receptor.
). VpreB
interacts with VH of the μH chain, Cλ5
displaces BIP and induces an Ig-domain structure in CH1
(○, green), forms a disulfide bridge and thus, the pre-B
cell receptor.