Figure 7.
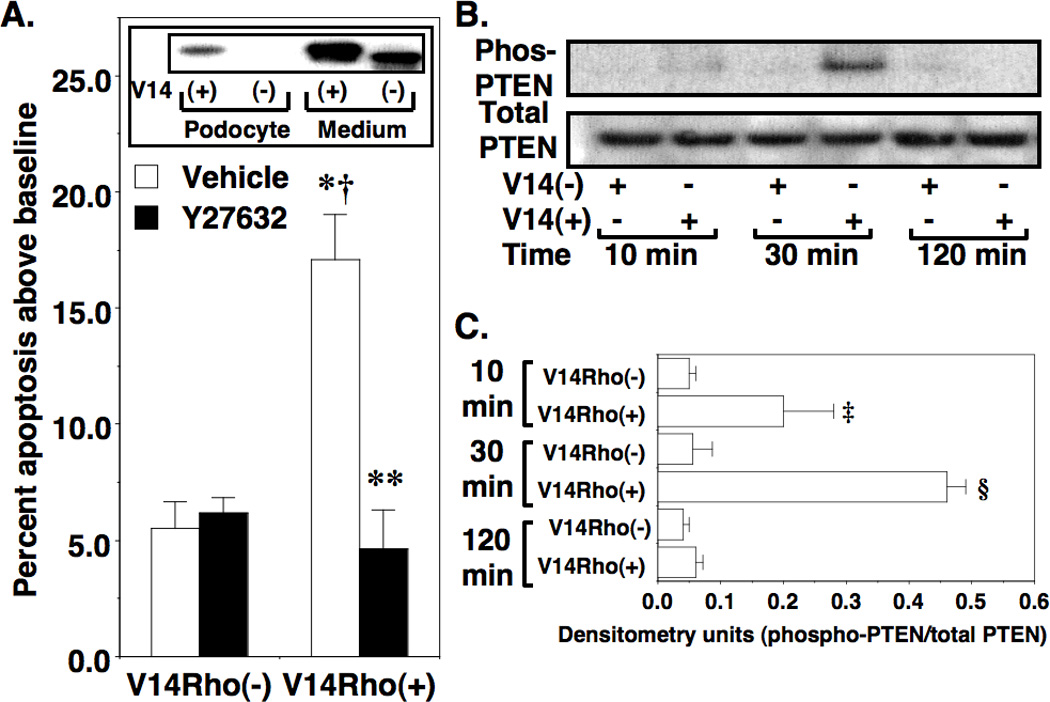
Effect of V14Rho(+) on podocyte apoptosis. In panel A, treatment with V14Rho(+) significantly increased podocyte apoptosis compared to cells treated with V14Rho(−), and Y27632 significantly reduced podocyte apoptosis induced by V14Rho(+). Immunoblotting of the HA-tagged V14Rho proteins in either culture medium or podocyte lysates is shown in the inset. The HA-tagged V14Rho(+) was effectively transduced into cultured podocytes. There is a slight difference in molecular size of V14Rho(+) and V14Rho(−) due to the presence or absence of the TAT sequence. In panel B, total PTEN and phospho-PTEN levels were assessed in immortalized podocytes after treatment with V14Rho(+) or V14Rho(−). Densitometric quantitation of the immunoblots is shown in Figure C. Phospho-PTEN levels were significantly increased in cells treated with V14Rho(+) at the 10-minute and 30-minute time points. Four to 7 samples were studied per group for the apoptosis experiments. Four to 5 samples were studied per group for the immunoblotting studies. *P<0.001 vs cells treated with V14Rho(−) and vehicle, †P<0.01 vs cells treated with V14Rho(−) and Y27632, **P<0.001 vs cells treated with V14Rho(+) and vehicle ‡P<0.05 or §P<0.01 vs vs cells treated with V14Rho(−)
