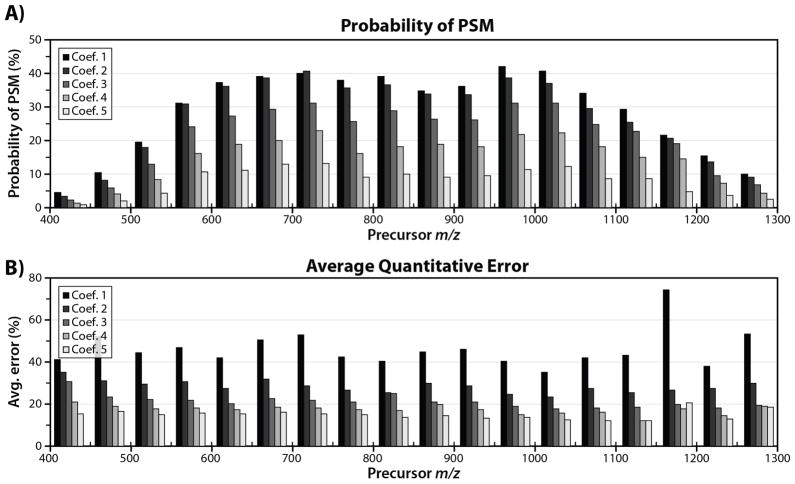
Figure 4.
Average probability of error (A) and average quantitative error (B) binned by precursor m/z value for IRMPD experiments. For each experiment, the RF amplitude was held constant, resulting in a fixed low-mass cutoff (LMCO) and dynamic precursor q- value. IRMPD activation times were set in a data-dependent manner by multiplying the precursor m/z by a coefficient. Using this strategy, we are able to normalize IRMPD PSM production and quantitative accuracy across a wide range of precursor m/z values. Coefficients 1 – 5 correspond to increased IRMPD irradiation time. Increasing irradiation time increases secondary dissociation, resulting in better quantitative accuracy, but confounding spectral interpretation.