Figure 6.
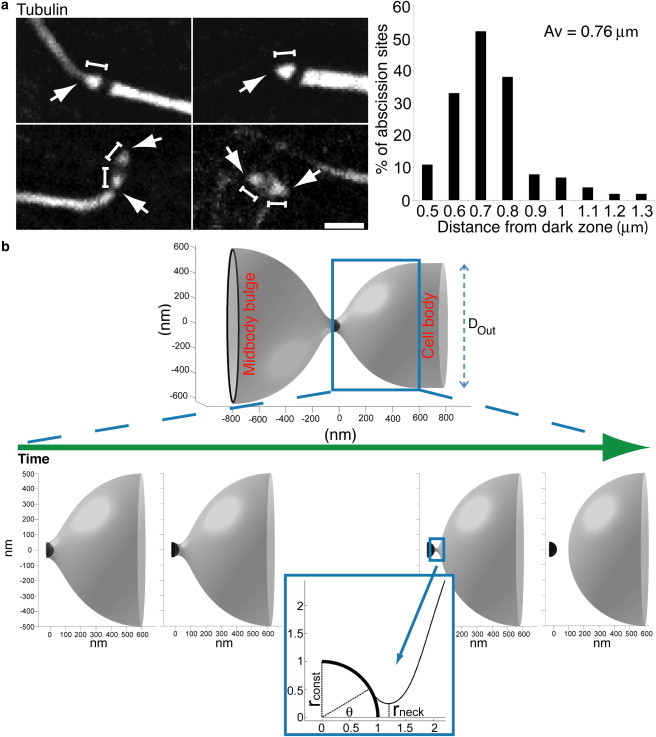
Experimental verification of the equilibrium distance and theoretical modeling of ESCRT-III-mediated membrane fission in cytokinesis. (a) Testing the equilibrium distance in cells undergoing abscission. The distance between the end of the midbody dark zone and the site of microtubule constriction was measured in synchronized MDCK cells stained with anti-α-tubulin antibodies (white). Images on the left are representative examples for the different types of intercellular bridges chosen for this analysis. Arrows represent the sites of constriction/scission and bars represent the distances measured. The histogram to the right shows the distribution of the measured distances. A preferred distance of 0.6–0.8 μm between the edge of the dark zone and the site of microtubule constriction was observed in the majority of intercellular bridges that were examined. The total average for all measurements was 0.76 ± 0.15 μm. Data were obtained from two independent experiments. n = 157. Scale bars = 2 μm. (b) Computational analysis of ESCRT-III-mediated final fission in cytokinetic abscission. Upper panel shows entire system configuration after constriction of the abscission site to a 0.1 μm diameter for better visualization. The diameter of the cell body is taken Dout = 1 μm. Framed window represents the membrane neck committed to fission described in details in the image sequence below. Lower panel shows the computed configurations of the membrane neck formed at sequential stages of the membrane attachment to the dome-like end-cap of the ESCRT-III fission complex at the abscission site. The first to third panels (left to right) represent the neck configurations at increasing attachment angles θ = 0°, 30°, 62°, respectively. The fourth panel shows a postfission state where the midbody and cell are separated. Inset: zoom into the constriction site. The dome radius rconst is taken to be10 times smaller than the radius rout of the tube connecting the fission site to the body of the daughter cell.
