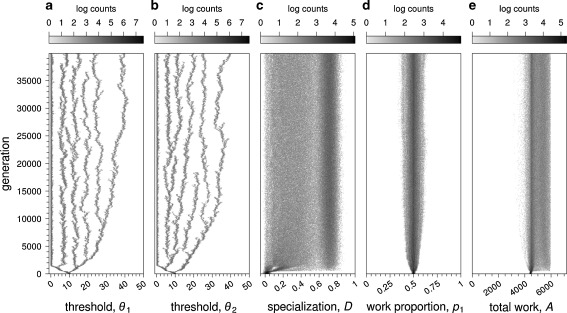
Fig. 4.
Evolutionary simulation of the response threshold model, when switching tasks is costly (c = 2) and β = 0.5, under the standard fitness scenario (Eq. 3). The setup of the simulations and the graphical conventions are identical to Fig. 2. Both thresholds diverged quickly into equally spaced multiple branches (a, b). Worker specialization increased quickly in the first 500 generations, with 55.6 ± 2.8 % (mean ± SD) of the colonies having a D value larger than 0.5 (c). The work distribution varied among colonies around p 1 = 0.5 (d). In the first generations, colonies have perform a low amount of work (e), reflecting the fact that workers switching tasks have to stay idle for c = 2 time periods. Part of the population recovers from this cost by evolving specialization