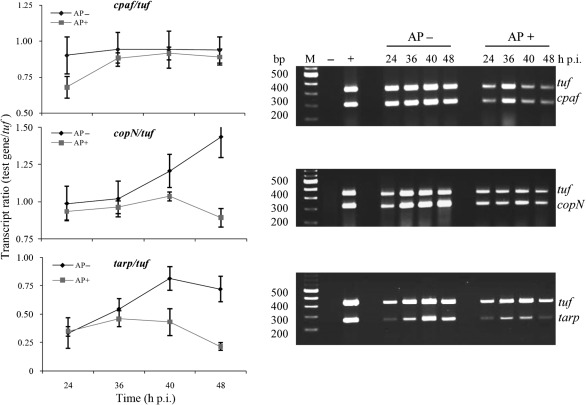
Fig. 6.
Transcription analysis of chlamydial genes in C. trachomatis-infected HeLa cells by dual-complex RT-PCR. The right panels show ethidium-bromide-stained agarose gels indicating the transcript levels of the tuf, cpaf, copN and tarp genes from C. trachomatis-infected HeLa cells exposed to ampicillin (AP+) or under normal growth conditions (AP−). Genomic DNA extracted from purified C. trachomatis EBs was used as a positive control to demonstrate that in this dual-complex reaction the two primer pairs amplified the targets with similar efficiencies (lane +). RNA isolated from uninfected HeLa cells was used as a negative control (lane −). A fixed quantity of total RNA (host cell RNA+C. trachomatis RNA) isolated at the indicated times was treated with DNase I and subjected to RT-PCR. Graphs depicting the mean±sd of three independent experiments for each primer set are shown on the left. These show the ratio of cpaf, copN and tarp transcripts to the tuf transcripts at different time points p.i. as revealed by the RT-PCR analysis in normal infected cultures or cultures exposed to ampicillin. Note the decrease in transcript levels that occurred in ampicillin-exposed samples due to bacterial growth retardation.