Figure 1.
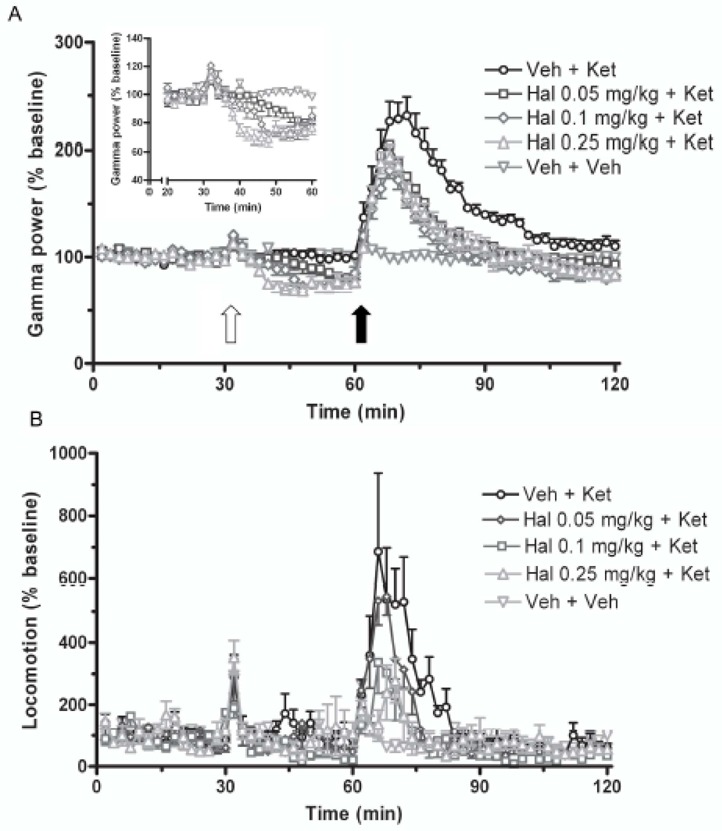
Effects of haloperidol on ketamine-induced elevations in gamma power and locomotor activity in rats. (A - insert) Haloperidol (0.05 – 0.25 mg/kg sc) dose-dependently depressed ongoing gamma power by up to 30% during the 30 min pretreatment phase of the recordings, compared to vehicle treatment. (A) Haloperidol significantly but incompletely reduced the rise in gamma power induced by ketamine (5mg/kg sc), compared with vehicle pretreatment. This effect was not dose-dependent. (B) Pretreatment with haloperidol dose-dependently suppressed ketamine induced hyperlocomotor activity, conmpared with vehicle pretreatment. Data represent mean ± S.E.M.; n=8. Open arrow indicates timing of haloperidol administration, and closed arrow indicates ketamine administration.
