Figure 5. CRKL-induced cell transformation requires SOS1-RAS-RAF.
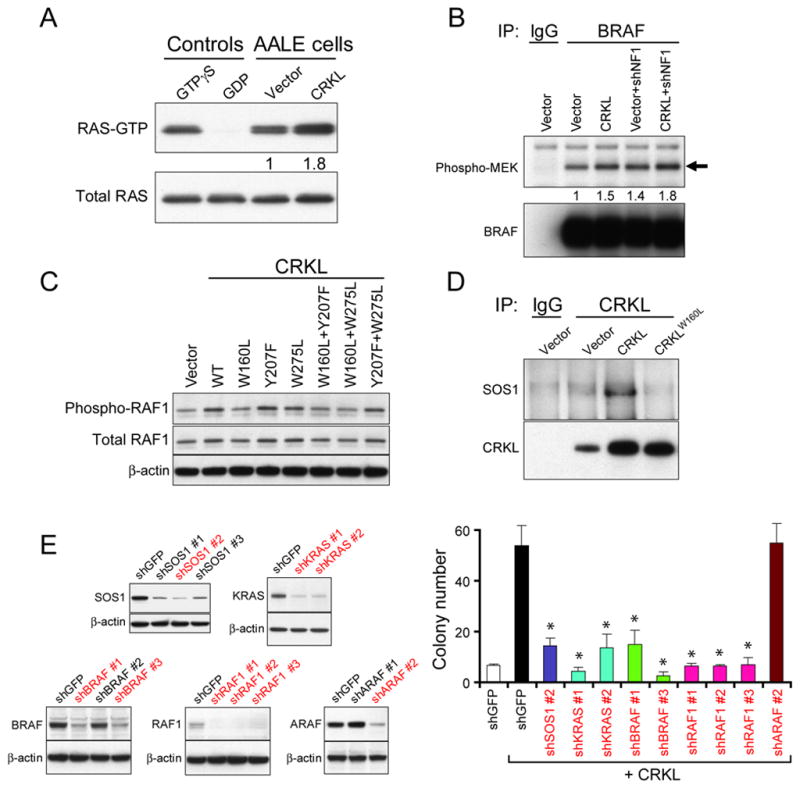
(A) Overexpression of CRKL increased RAS activity. The levels of GTP-bound RAS in AALE cells overexpressing a control vector or CRKL were measured by a pull-down assay followed by immunoblotting for RAS. Total RAS levels in total lysates were used as loading control. Positive and negative technical controls were obtained by incubating the total lysates with non-hydrolyzable analog of GTP (GTPγS) or GDP, respectively, before pull-down assays.
(B) Overexpression of CRKL increased in vitro BRAF kinase activity. The BRAF proteins in AALE cells expressing indicated constructs were isolated by immunoprecipitation. The kinase activity was assessed by incubating with substrate proteins (MEK1). Immunoblots of phospho-MEK1 and BRAF proteins in the isolated BRAF immune complexes after kinase activity assay are shown.
(C) Immunoblot of phospho-S338-RAF1 in AALE cell lines overexpressing wildtype or mutant CRKL.
(D) Interaction between CRKL and SOS1 in AALE cells overexpressing CRKL. CRKL immune complexes were isolated followed by immunoblotting for SOS1 or CRKL proteins in AALE cells expressing indicated constructs.
(E) CRKL-induced anchorage independent growth required SOS1-RAS-BRAF/RAF1 signaling. Left, Immunoblots of SOS1, KRAS, BRAF, RAF1 or ARAF proteins in CRKL-overexpressing AALE cell lines expressing a control shRNA targeting GFP or each gene-specific shRNA. ShRNAs that suppressed more than 50% of target protein levels were marked in red color. Right, Anchorage independent growth of AALE cells expressing indicated constructs. Colony number indicates colonies greater than 0.2 mm in diameter 4 weeks after plating. Data represent mean + s.d. of six replicate determinations from two independent experiments. * indicates p<0.0001 as compared to cells expressing CRKL and shGFP.
