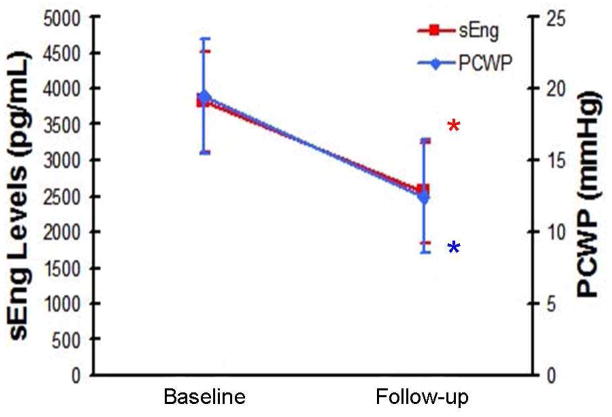
Figure 4.
Reduced sEng levels correlate with reduced PCWP. Compared to baseline values, sEng levels were significantly reduced after 48 hours of diuretic therapy (*3830+330 vs 2540+1060pg/mL, baseline vs follow-up, respectively, p<0.001) and corresponded with reduced PCWP (*19.5+3.1 vs 12.5+4.5mmHg, baseline vs follow-up, respectively, p<0.001). Percent change in sEng was strongly associated with the percent change in LVEDP (R=0.75, p=0.008). In this group, levels of ANP and BNP were also reduced after diuretic therapy (ANP: 10.5+4.7 vs 5.2+1.9 ng/mL, respectively p=0.02; BNP: 8.8+2.5 vs 6.2+1.7 ng/mL,, respectively, p=0.05). [ANP: atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; LVEDP: left ventricular end-diastolic pressure; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; PCWP: pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; sEng: soluble endoglin]