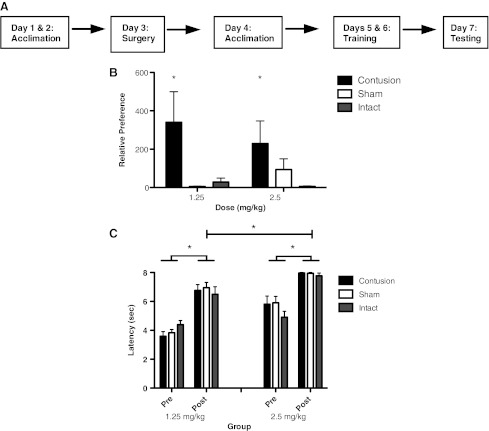
FIG. 1.
For the conditioned place preference assessments, the subjects were trained according to the timeline depicted in A. They were exposed to a neutral context for 2 days prior to surgery, and again 1 day following surgery. Training took place over 2 consecutive days, and testing on a third day. As shown in B, contused subjects developed an increased preference for the morphine-paired context, relative to sham and intact controls, after only two morphine-context pairings. Relative preference was determined using: (time spent in drug-paired context+1)/(time spent in vehicle-paired context+1). Morphine administration produced analgesia in all groups, but was more robust in the 2.5-mg/kg group (C; *p<0.05).