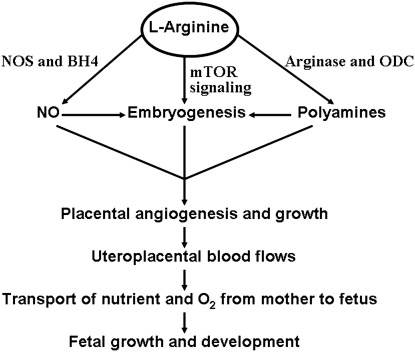
FIG. 9.
Role of L-arginine in enhancing fetal growth and development in response to maternal undernutrition or overnutrition. Through the tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)-dependent synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) and production of polyamines from arginine-derived ornithine as well as activation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) signaling pathway, L-arginine can promote embryogenesis and placental vascular growth. Antioxidants are essential to maintain sufficient levels of BH4 in cells for NO synthase (NOS). Enhancement of uteroplacental blood flow ensures adequate transport of nutrients and oxygen from mother to fetus to support fetal growth and development under the conditions of maternal malnutrition. ODC, ornithine decarboxylase.