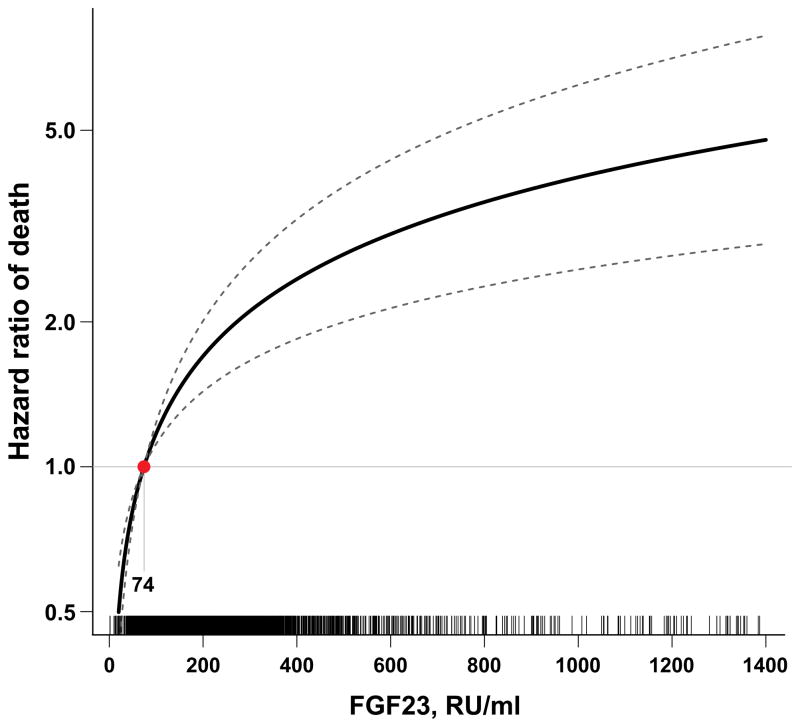
Figure 2. Multivariable-adjusted hazard function for death according to FGF23 levels.
The median FGF23 level within the lowest FGF23 quartile (74 RU/ml) served as the referent value (hazard = 1). The model was stratified by center and adjusted for age, sex, race, ethnicity, estimated glomerular filtration rate, natural log-transformed urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio, hemoglobin, serum albumin, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, diabetes, smoking, low density lipoprotein, history of coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease, and use of aspirin, beta-blockers, statins, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, and serum calcium, phosphate and natural log-transformed parathyroid hormone. Tick marks on the x axis indicate individual observations at corresponding levels of FGF23. This figure is reproduced from Isakova et al [25], with permission from the American Medical Association. Copyright c [2011] American Medical Association. All rights reserved.