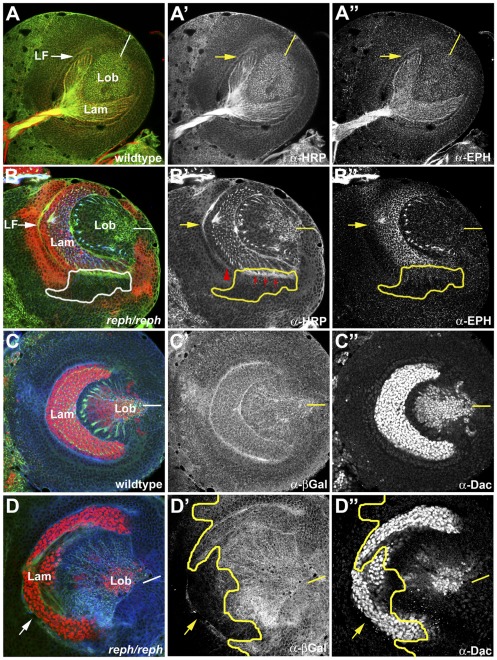
Figure 7. reph loss-of-function suggests cell autonomous regulation of Eph expression.
A requirement for reph in optic lobe development was assessed by generating homozygous somatic rephk8617A clones by the FLP, FRT method. Mutant clones were marked by loss of expression of an arm-lacZ reporter (anti-βgal, red in B, blue in C and D). Overall optic lobe architecture was revealed by anti-HRP staining (green color in all panels, shown alone in A′ and B′). A,A′,A″) A wild type specimen illustrating the normal distribution of Eph expression in the lamina. B,B′,B″) A specimen harboring a homozygous rephk8617A clone (white or yellow outlines) along the ventral margin of the lamina displayed reduced Eph expression (anti-Eph, blue in B, shown alone in B″) and incomplete LF formation (red arrowhead in B′). To assess potential pleiotrophic effects of rephk8617A on lamina development, rephk8617A clones were stained for dachshund, a marker of lamina neurogenesis (anti-Dac, red color in C and D, shown alone in C″ and D″). C,C′,C″) A wild type specimen highlighting Dac expression in the lamina. D,D′,D″) In the specimen shown, a large rephk8617A clone encompassed most of the ventral lamina (yellow outline) indicated by loss of lac-Z staining (blue). Dac expression was normal within the clone. Dorsal is up and ventral is down in all panels. Abbreviations: lamina (lam), lamina furrow (LF), lobula (lob). Yellow bars in A″–D″ indicate the position of the midline.