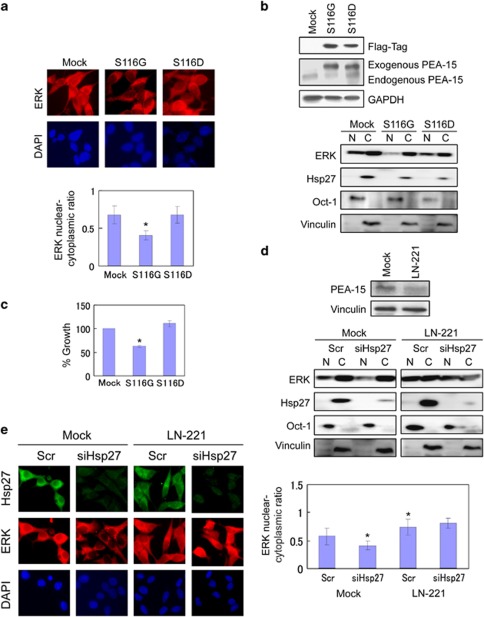
Figure 2.
ERK translocation is regulated by PEA-15 in phosphorylation-dependent manner in LNCaP cells. (a) PEA-15 regulates ERK translocation. LNCaP cells transfected with a non-phosphorylatable mutant (S116G) or a phosphomimetic mutant of PEA-15 (S116D). The nucleocytoplasmic distribution of ERK was assessed in LNCaPmock and LNCaPHsp27 cells by immunofluorescence microscopy. Cells were immunostained with anti-ERK (red) antibodies. DAPI (blue) nuclear counterstaining was used to define the cell nuclei. (b) Levels of exogenous and endogenous PEA-15 proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Flag and anti-PEA-15 antibodies. (c) Growth effect of LNCaP cells expressing non-phosphorylatable (S116G) and phosphomimetic (S116D) PEA-15 mutants. Cell growth rates of LNCaP cells were compared by crystal violet assay. (d) Protein levels of ERK, Hsp27, Oct-4 and vinculin were determined in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of cell lysates derived from LN-221 versus LNCaPmock cells treated with Scr or siHsp27 by immunoblotting. shRNA-mediated silencing of PEA-15 was examined by immunoblotting. (e) ERK nuclear translocation in LNCaP cells is regulated by PEA-15. The nucleocytoplasmic localization of ERK was analyzed in LN-221 versus LNCaPmock cells treated with Scr or siHsp27 by immunofluorescence microscopy as described above. Cells were immunostained with anti-Hsp27 (green) and anti-ERK (red) antibodies. DAPI (blue) nuclear counterstaining was used to define the cell nuclei. The mean fluorescence ratios FN/C are shown for ERK. Values shown represent mean±S.D. The symbol ‘*' denotes statistical significance (P<0.05)