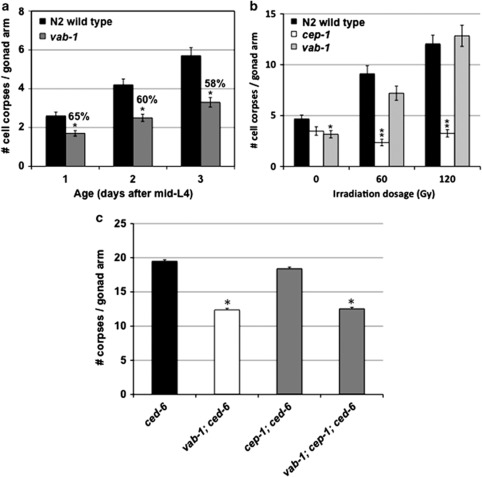
Figure 5.
vab-1 activity does not equally impact all germline cell death pathways. (a) Cell corpse quantification in a wild-type background over 3 days after the L4 larval stage. Apoptosis is similarly compromised in vab-1(dx31) mutants as animals age (n=40; Mann–Whitney test with ties adjustment, *P<0.001). The numbers over the vab-1 columns represent the percentage of corpses relative to the N2 wild-type animals at the same age. (b) Germ-cell corpse counts after γ-irradiation, resulting in activation of the DNA-damage pathway. A dose-dependent increase in apoptosis was lost in the cep-1/p53(gk138) mutant strain (n: all radiation doses, 29) as compared with the N2 wild type (n: 0 Gy, 28; 60 Gy, 29; 120 Gy, 29), but not in the vab-1(dx31) mutants (n: 0 Gy, 29; 60 Gy, 28; 120 Gy, 29; Student's t-test, **P<0.001; *P=0.014). Experiment performed under ced-10(RNAi) engulfment-defective conditions. (c) Comparison of germ-cell corpse counts between vab-1(dx31); cep-1(gk138) double mutants and the respective single mutant strains. All animals were ced-6(n1813) engulfment-defective. Loss of cep-1 activity had no impact on corpse numbers in wild-type or vab-1 mutant worms, while vab-1 mutants displayed reduced corpse numbers in cep-1 and wild-type animals (n: ced-6, 37; vab-1, 29; cep-1; ced-6, 36; vab-1; cep-1; ced-6, 39; Student's t-test, *P<0.005). All graphs summarize data from at least three independent experiments and represent the mean±S.E.M.