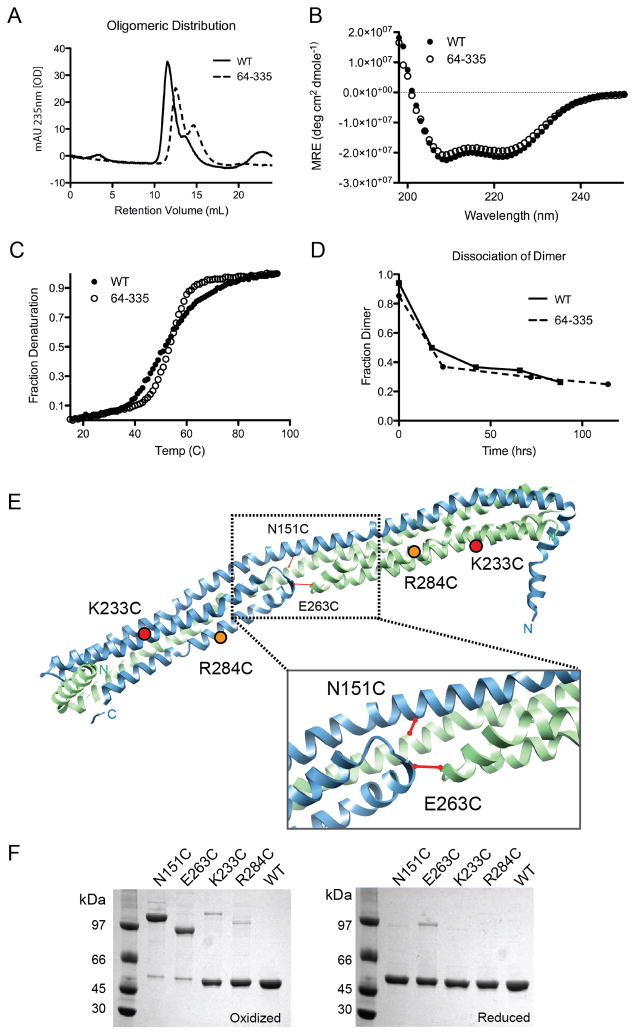
Figure 2.
Ability of apoA-IV64-335 to model apoA-IVWT. (A) Isolated apoA-IVWT and apoA-IV64-335 dimer incubated at 37°C in PBS for 24hrs and analyzed by SEC (dimers at 11–12 ml, monomers at 14–15 ml). (B) Far UV CD spectra of dimeric apoA-IVWT and apoA-IV64-335 at 0.85μM at 25°C. (C) Thermal denaturation of both forms as monitored by CD at 222nm. (D) Rate of dimer disassociation over time measured by SEC for both apoA-IVWT and apoA-IV64-335. (E) Introduction of single Cys point mutations (N151C, E263C, K233C and R284C) to test the dimer model. Predicted disulfide bond formation in WT apoA-IV based on the crystal structure is indicated with a solid line. (F) SDS-PAGE of point mutations of apoA-IVWT designed in (D) that were purified under reducing conditions (right) and then oxidized to allow disulfide bond formation (left), stained with coomassie blue. See also Figure S2 and Table S1.