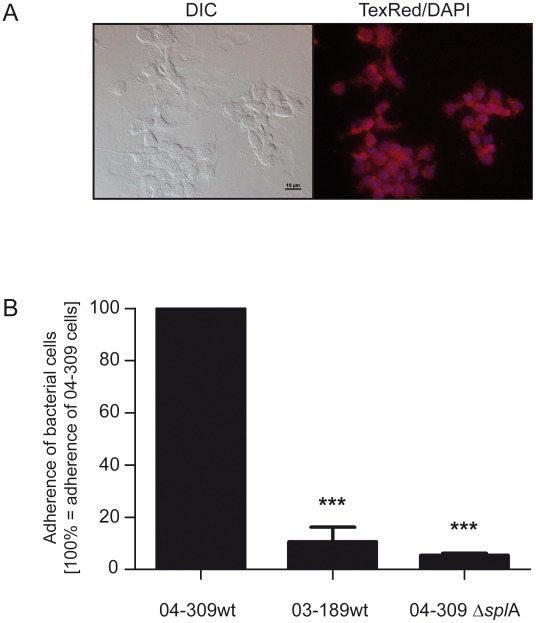
Figure 5. Adhesion of P. larvae 04-309 ΔsplA and P. larvae 04-309 wild-type to primary pupal gut cells.
(A) Vitality of primary pupal gut cells after 6 days of cultivation was analyzed using Mitotracker Red FM (Invitrogen) to specifically label active mitochondria indicative for live cells. Cells were microscopically analyzed using Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) (left) as well as TexRed (mitochondria) and DAPI (nuclei) filters to visualize fluorescence signals (right). (B) Percentage of P. larvae 03-189 wild-type (03-189 wt; ERIC I, naturally SplA-deficient) and P. larvae 04-309 ΔsplA (SplA knockout mutant) associated to pupal gut cells after 60 min of incubation, extensive washing, and cell lysis; results are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent-experiments and are related to cell-associated bacteria of the wild-type strain P. larvae 04-309 (04-309 wt; ERIC II), i.e. the amount of P. larvae 04-309 cell-associated bacteria in each experiment equalled 100%. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Bonferroni post-hoc test (***p<0.001).