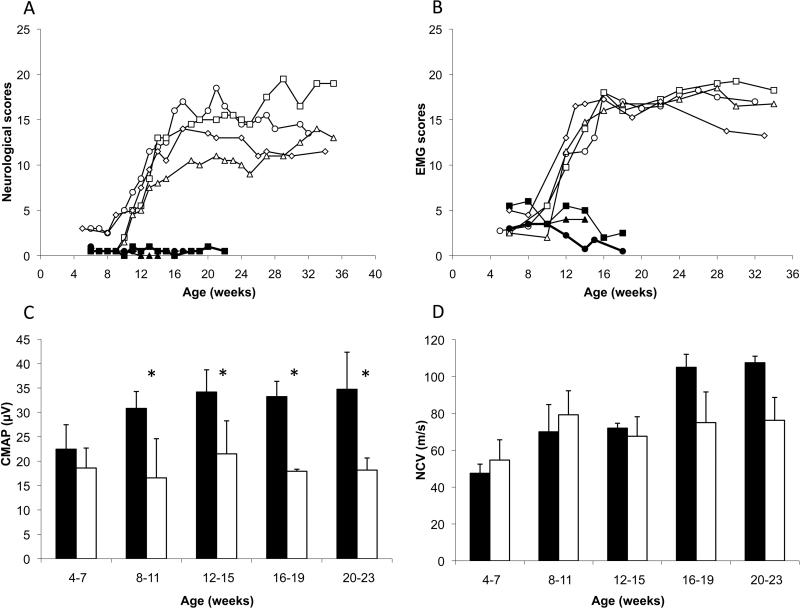
Figure 2.
Evolution of (A) neurological signs and (B) electromyographic (EMG) abnormalities, scored according to severity, in 3 normal cats (solid symbols) and 4 affected (open symbols) from 4 to 36 weeks of age. (C) Compound muscle action potentials (CMAP) measured in soleus muscle after a stimulation of the sciatic nerve. (asterisks indicate statistical significance at p<0.05), and (D) nerve conduction velocities (NCV) of the sciatic nerve in normal (solid bars) and affected (open bars) cats.