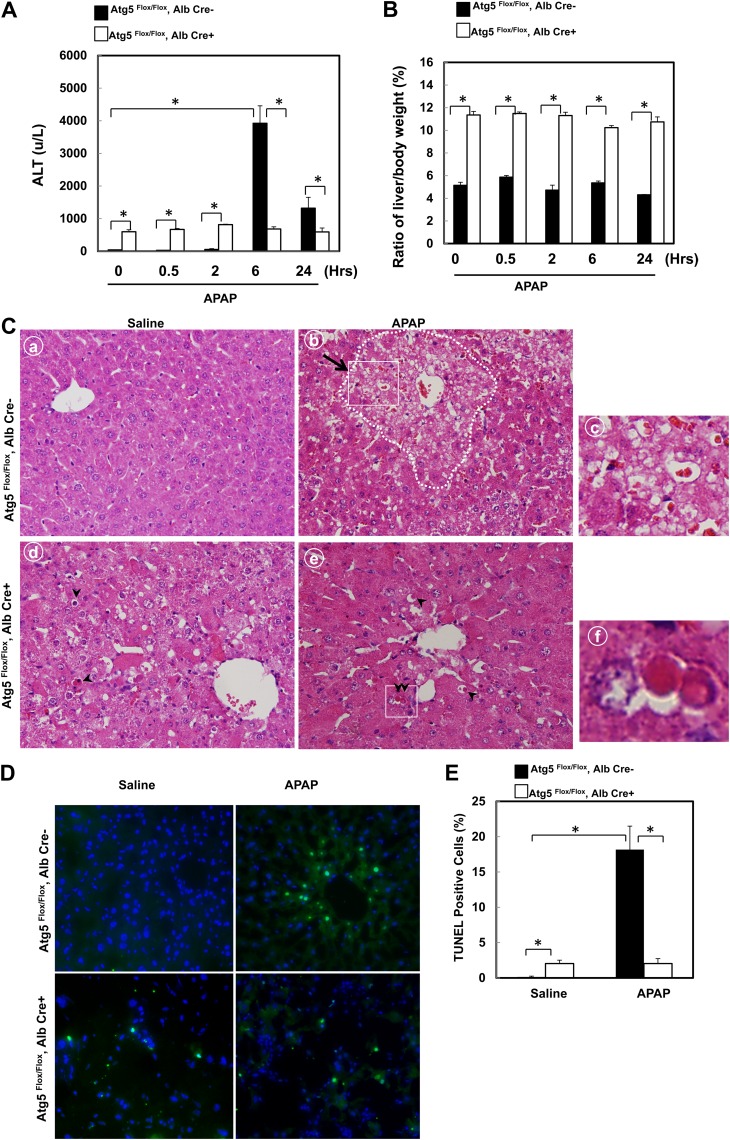
FIG. 2.
Mice with the loss of Atg5 are resistant to APAP-induced liver injury. Two-month-old Cre-negative and Cre-positive Atg5 Flox/Flox mice were injected with saline or APAP (500 mg/kg) for 0, 0.5, 2, 6, and 24 h. Serum ALT levels (A) and ratio of the liver to body weight (B) were determined. Data are means ± SE (n ≥ 3). *p < 0.05. One-way ANOVA analysis with Scheffé's post hoc test. (C) Cre-negative and Cre-positive Atg5 Flox/Flox mice were injected with saline or APAP (500 mg/kg) for 6 h. Representative photographs of hematoxylin and eosin staining are presented. Panels a–c: Cre-negative Atg5 Flox/Flox mice. Panels d–f: Cre-positive Atg5 Flox/Flox mice. Dotted area in panel b: centrilobular necrosis. Arrow: necrotic cells. Arrow heads: apoptotic cells. Panels c and f were enlarged photographs from panels b and e, respectively. (D) Cre-negative and Cre-positive Atg5 Flox/Flox mice were injected with saline or APAP (500 mg/kg) for 6 h. Representative photographs of TUNEL staining are presented. (E) The number of TUNEL-positive nuclei and total nuclei were quantified from three random fields of three different mice. Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 3). *p < 0.05. One-way ANOVA analysis with Scheffé's post hoc test.