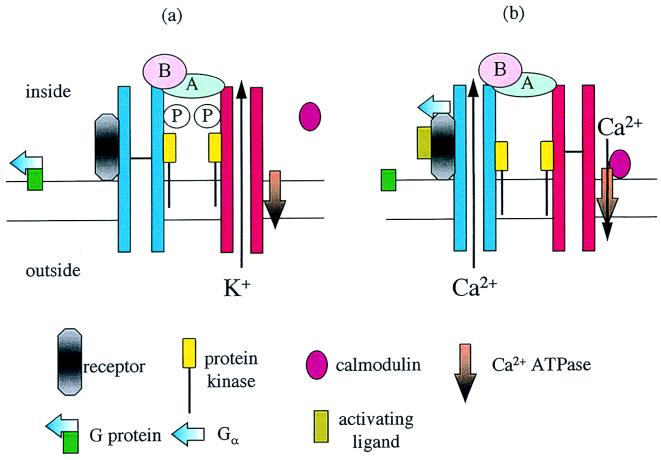
Figure 1.
Suggested structure of a transducon on the plasma membrane. In the K+-transporting mode, (a), the major constituents remain bound together, except for calmodulin. When a ligand binds to the receptor (b), it is suggested that the receptor and Gαa subunit from a G protein remain bound together, briefly activating the Ca2+ channel. The B subunit of calcineurin situated at the Ca2+ channel mouth responds to the high Ca2+ concentrations and activates the A subunit. Dephosphorylation inhibits the K+ channel, and dephosphorylation of the Ca2+ channel prolongs opening. Calmodulin binds to the ATPase regulating Ca2+ outflow from the cell but only at a suitable distance from the channel mouth and where Ca2+ concentrations are lower.