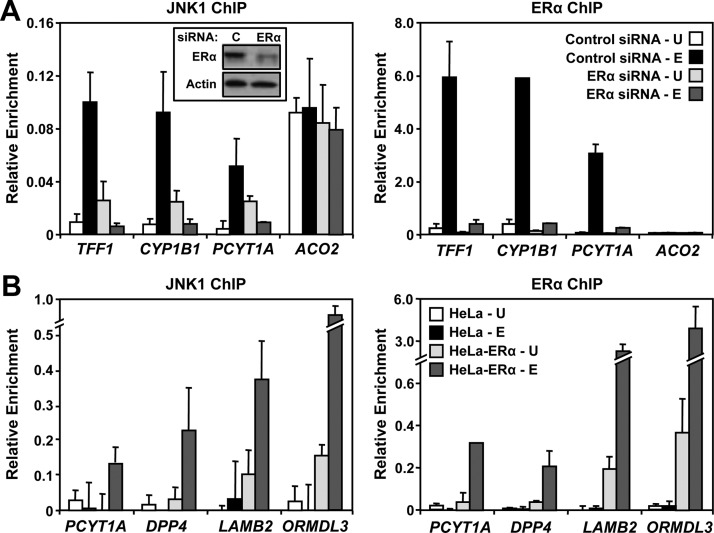
Fig. 4.
ERα binding at target promoters is required for JNK1 recruitment. A, MCF-7 cells were transfected with control or ERα siRNAs. Sixty hours after transfection, the cells were treated with vehicle (U) or E2 (E) for 45 min and collected for Western blotting or ChIP-qPCR analyses. ChIP-qPCR analyses of the E2-dependent JNK1 (left) and ERα (right) binding to three “JNK1-recruited” gene promoters (TFF1, CYP1B1, and PCYT1A) and one “JNK1-constitutive” gene promoter (ACO2) are shown. Each bar represents the mean ± sem, n = 3. Inset in left panel, Western blot analysis of siRNA-mediated ERα knockdown vs. control (C) is shown with β-actin as a loading control. B, ChIP-qPCR analyses of E2-dependent JNK1 (left) and ERα (right) binding to four gene promoters (PCYT2, DPP4, LAMB2, and ORMDL3) in parental HeLa cells and HeLa cells stably expressing ERα (HeLa-ERα). The cells were treated with vehicle (U) or E2 (E) for 45 min and analyzed by ChIP-qPCR. Each bar represents the mean ± sem, n = 3.