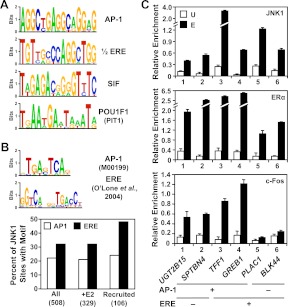
Fig. 5.
Motif analysis of JNK1 peaks. A, Unbiased search for DNA sequence motifs enriched under the JNK1-bound regions in the E2-treated condition using MEME. A selection of some of the most significantly enriched motifs are shown as web logos of the position weight matrices. Motif predictions were examined by TESS, as well visual inspection, to determine transcription factors that are most likely to bind to the indicated sequence, as indicated. B, Targeted search for AP-1 and ERα (i.e. ERE) binding motifs 1) under all JNK1 peaks in both vehicle- and E2-treated conditions, 2) JNK1 peaks in the E2-treated condition, and 3) under all JNK1-recruited peaks. Top, The position weight matrices used in the targeted search for AP-1 and ERα binding motifs are shown as web logos. The AP-1 position weight matrix is from TRANSFAC, whereas the ERα position weight matrix is based on information from O'Lone et al. (70). Bottom, The position weight matrices for the AP-1 and ERα motifs were used with MAST to map the location of the motifs under JNK1 peaks in a directed search. The percent of JNK1-binding sites in each of the indicated groups with an AP-1 or ERα motifs motif is shown. C, c-Fos localizes with JNK1 and ERα at target promoters containing an AP-1 binding motif. ChIP-qPCR analyses of JNK1, ERα, and c-Fos binding at JNK1- and ERα-recruited regions before (U) and after estrogen (E) treatment are shown. The UGT2B15, SPTBN4, TFF1, and GREB1 gene promoters contain at least one predicted AP-1 motif under the JNK1 peak. The TFF1, GREB1, and PLAC1 promoters, as well as the BLK44 distal enhancer (58), contain at least one ERE under the JNK1 peak. Each bar represents the mean ± sem, n = 3.