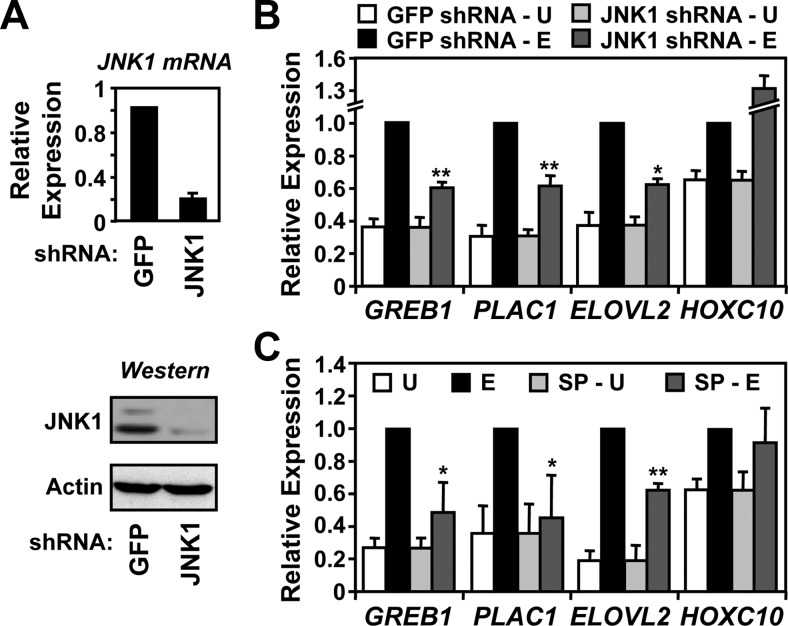
Fig. 6.
JNK1 activity is required for full estrogen-dependent transcriptional responses at estrogen target promoters. A, JNK1 was stably knocked down in MCF-7 cells by retroviral-mediated delivery of an shRNA construct followed by drug selection. An shRNA construct targeting GFP was used as a control. Top, Analysis of JNK1 mRNA expression by RT-qPCR. β-Actin mRNA was used as an internal control. Each bar represents the mean ± sem, n = 3. Bottom, Analysis of JNK1 protein levels by Western blotting. β-Actin was used as a loading control. B, Effect of JNK1 knockdown on estrogen-dependent gene expression. The E2-regulated expression of four JNK1-recruited genes (GREB1, PLAC1, ELOVL2, and HOXC10) in control (GFP) and JNK1 knockdown MCF-7 cells was monitored by RT-qPCR before (U) and after (E) a 3-h treatment with E2. Each bar represents the mean ± sem, n = 3. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student's t test vs. corresponding E2 control. C, Effect of inhibiting JNK catalytic activity on estrogen-dependent gene expression. The E2-regulated expression of the four JNK1-recruited genes shown in B was examined by RT-qPCR in the absence or presence of the JNK inhibitor SP for 1 h, before a 3-h treatment with vehicle (U) or E2 (E). Each bar represents the mean ± sem, n = 3. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; Student's t test vs. corresponding E2 control.