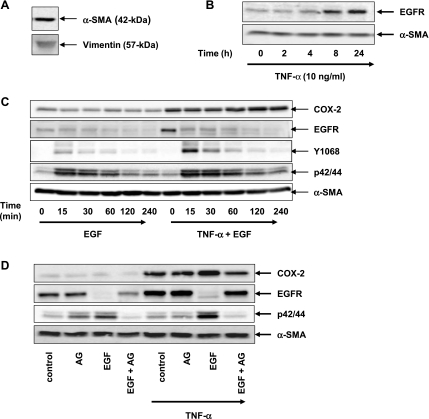
Fig. 7.
TNF-α increases EGFR expression and enhances EGF-mediated COX-2 expression in human colonic myofibroblasts. A: cell lysates of primary colonic myofibroblasts isolated from human colon tissue were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies that detect vimentin and α-SMA. Results represent n ≥ 3 experiments. B: confluent primary colonic myofibroblasts were washed and equilibrated in serum-free media for 30 min and then incubated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α over various times (2, 4, 8, and 24 h, as indicated). Cell lysates were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot using an antibody that detects EGFR protein. Results represent n ≥ 3 experiments. Equal protein loading was verified using an antibody that detects α-SMA. C: primary colonic myofibroblasts were incubated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 18 h and then were exposed to 5 ng/ml EGF at various times (15, 30, 60, 120, and 240 min, as indicated). Cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot using antibodies that detect COX-2, EGFR, EGFR phosphorylation at Y1068, and p42/44 MAPK phosphorylation. Equal protein loading was verified using an antibody that detects α-SMA. Results represent n ≥ 3 experiments. D: cultures of primary colonic myofibroblasts were pretreated for 1 h with the EGFR inhibitor 1 μM AG1478 before exposure to 5 ng/ml EGF for 4 h in the presence or absence of an 18-h incubation with 10 ng/ml TNF-α. Cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot using anti-COX-2 antibody and an antibody that detects EGFR and p/42/44 MAPK phosphorylation. Similar results were obtained in ≥3 independent experiments for each condition. Equal protein loading was verified using an antibody that detects α-SMA.