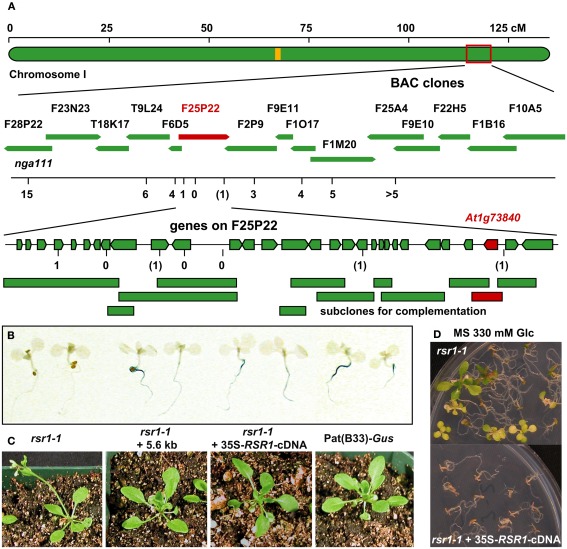
Figure 5.
Identification of RSR1 and complementation of mutant phenotypes. (A) Schematic view of chromosome I with two subsequent enlargements of the region around RSR1. BAC clones of the region between nga111 and ADH were screened for markers polymorphic between C24 and Col-0. The second enlargement shows the position and orientation of annotated genes on BAC clone F25P22. Vertical black lines indicate the positions of markers used for the mapping of rsr1-1. The numbers below the markers are the numbers of recombination events between RSR1 and the respective marker, observed in a population of 1315 F2 plants from a cross between rsr1-1 and Col-8. Numbers in brackets indicate that a double recombination event to the left and right of the respective marker was observed. Green bars below BAC F25P22 indicate genomic fragments that could not complement rsr1-1. The single complementing fragment in which At1g73840 is the only intact gene is shown in red. (B) GUS-staining in roots of seedlings grown in the presence of 90 mM sucrose demonstrated that sugar induction of the patatin class II promoter was lost in rsr1-1 plants, but restored by transformation with either the 5.6-kb genomic fragment shown above or the cDNA of At1g73840 under control of the CaMV 35S promoter. (C) Normal flowering was restored in rsr1-1 plants expressing a wildtype copy of At1g73840. (D) Overexpression of the At1g73840 cDNA in rsr1-1 reverted the gin-phenotype.