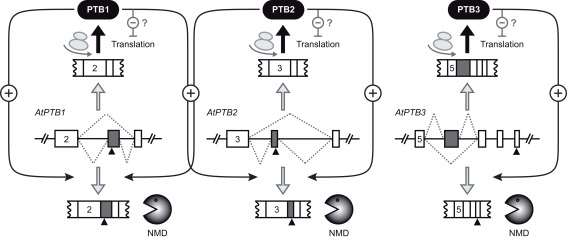
Figure 2.
Auto- and cross-regulation of the ArabidopsisPTB homologs. Exon-intron organizations of the Arabidopsis genes AtPTB1, AtPTB2, and AtPTB3 are shown for the regions giving rise to alternative splicing (dotted lines). Exons and introns are depicted as boxes and lines, respectively. Gray boxes refer to cassette exons, which are either skipped or included. Numbers of first displayed exons are given for all three genes. Black triangles indicate premature termination codons, rendering the respective splicing variants degradation via nonsense-mediated decay (NMD, bottom). The splicing variants shown on top of each gene model are translated into PTB proteins, which can interfere with translation of PTB mRNAs (for simplicity, only the effect on their own mRNAs is shown). PTB proteins also trigger splicing of their own pre-mRNAs to the NMD target variants (auto-regulation). Additionally, cross-regulation between PTB1 and PTB2 occurs. The model is based on the work from Stauffer et al. (2010).