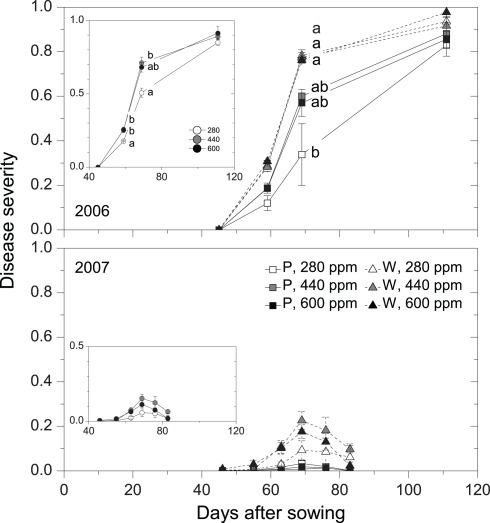
Figure 2.
Disease progress as affected by maternal CO2 concentration (280, 440, 600 ppm) and plant type (P = pink flowering, W = white flowering) in 2006 and 2007 (Case 2). Inserts show disease-progress affected by maternal CO2 only (Case 1). Disease severity was determined for each leaf and was subsequently added up for all leaves of a plant and expressed on a scale ranging between 0 and 1 (see Materials and Methods). Mean ± 1 SE, n = 3 model ecosystems. Non-identical letters indicate statistically significant differences among combinations of maternal CO2 treatments and plant type (main panels) or among maternal CO2 concentrations (inserts) as analyzed by the Tukey–Kramer HSD test (P ≤ 0.05 within mixed models, see Table 4). Sixty-three days after sowing in 2007, disease severity was significantly higher in 440-ppm progenies of plant-type W compared with all Type P progenies (Tukey–Kramer HSD test, P ≤ 0.05).