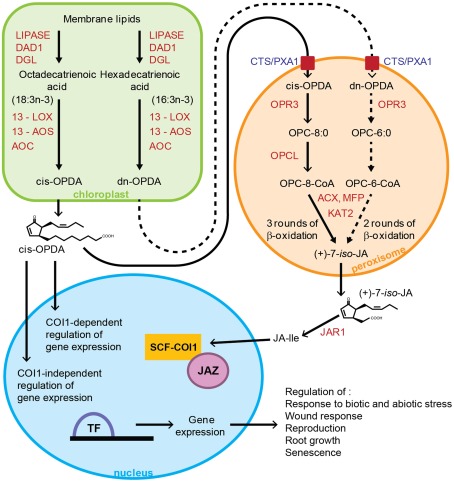
Figure 1.
Oxylipin biosynthesis pathway and signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. JA biosynthesis initiates in the plastid with release of octadecatrienoic acid or hexadecatrienoic acid from membrane lipids by lipases such as DAD1 and DGL. cis-OPDA and dn-OPDA are formed following sequential steps catalyzed by 13-LOX, 13-AOS, and AOC. cis-OPDA is transported to the peroxisome via the CTS transporter, where after reduction by OPR3, OPC-8:0 is formed. This is activated to its CoA ester by OPCL1, which then undergoes three rounds of β-oxidation catalyzed by ACX, KAT, and MFP to give (+)-7-iso-JA. JAR1 catalyzes formation of the amino acid conjugate JA-Ile from JA in the cytosol, which is the active form of the hormone involved in JA signaling. JAZ proteins repress expression of JA-responsive genes. In response to JA-Ile, the JAZ proteins are targeted by SCFCOI1 for degradation, thus leading to JA-dependent gene expression and ultimately the regulation of various physiological processes. The model proposes formation of the COI1-JAZ complex in the nucleus. cis-OPDA’s regulation of gene expression can be COI1-dependent or COI1 independent, although cis-OPDA has not been shown to promote binding of COI1 and JAZ. Enzyme names are shown in red. Dashed arrows indicate route to JA biosynthesis via dn-OPDA, where these steps are yet to be proven experimentally. DAD1, DEFECTIVE IN ANTHER DEHISCENCE1; DGL, DONGLE; 13-LOX, 13-lipoxygenase; 13-AOS, 13-allene oxide synthase; AOC, allene oxide cyclase; OPR3, 12-oxophytodienoate reductase3; OPCL1, OPC-8:CoA ligase1; CTS, COMATOSE; ACX, acyl CoA oxidase; KAT, 3-l-ketoacyl-CoA-thiolase; MFP, multifunctional protein; JA, jasmonic acid; cis-OPDA, cis-(+)-12-oxo-phytodienoic acid; dn-OPDA, dinor-oxo-phytodienoic acid; JA-Ile, jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine; COI1, CORONATINE-INSENSITIVE1; JAZ, jasmonate ZIM domain.