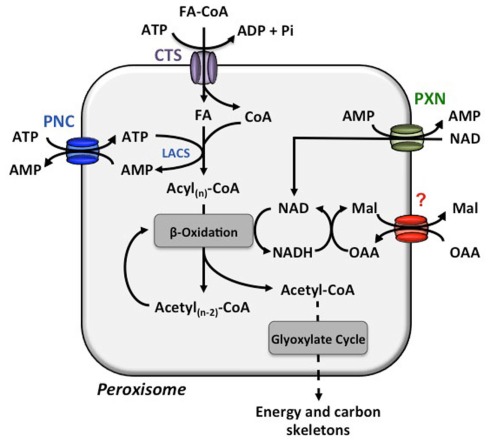
Figure 1.
Transport processes across the peroxisome membrane involved in β-oxidation. The COMATOSE (CTS) transporter facilitates the import of fatty acids from the cytosol to the peroxisomal matrix. The peroxisomal long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase (LACS) activates the free fatty acid (FA) to enter β-oxidation for a stepwise release of acetyl-CoA. For the energy consuming esterification of FAs with coenzyme A (CoA), ATP is required and provided by the import via the PCN proteins. The released AMP is the counter-substrate for the next round of ATP import. The reduction equivalent NAD is reduced during β-oxidation. The PXN transport most likely imports NAD to set-up a sufficient NAD pool in the peroxisomes and the main route for NADH regeneration is enabled via the not yet molecularly identified oxaloacetate (OAA)–malate (Mal) shuttle system.