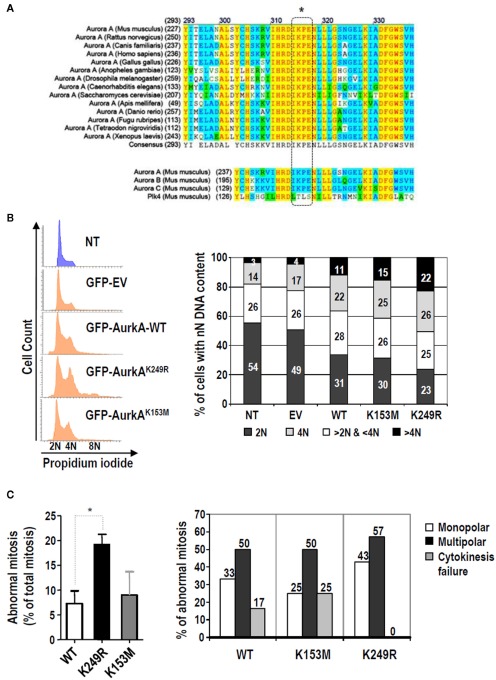
Figure 3.
Lack of SUMOylation of Aurora-A alters cell cycle regulation and increases the ratio of mitotic aberrations. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of Aurora-A proteins from different species using ClustalW softwarehttp://www.ch.embnet.org. The SUMO modification motif (dashed box) is highly conserved in all these Aurora-A proteins and in the other two Aurora family members, but it is not present in Polo-like kinase 4 (Plk4), a close mitotic relative of these mitotic kinases. (B) HeLa cells were transiently transfected with an empty vector expressing EGFP (EV) or with any of the three different EGFP-tagger Aurora-A isoforms (WT, K153, K249R). Forty-eight hours later, cell cycle profiles of transfected cells (EGFP-positive cells) and the non-transfected cells (NT; EGFP-negative) were obtained. The histograms and bar-graphs are representative of one of three independent experiments. (C) Evaluation of aberrant mitoses induced by Aurora-AK249R by video-microscopy using EGFP-tagged, Aurora-A stable cell lines. The left panel shows the percentage of abnormal mitoses. Three different stable clones were used for each Aurora-A variant. A total of 118, 81, and 46 mitoses were analyzed for the wild type, K153M and K249R variants, respectively. The bars show the average (±SE) of the percentage of abnormal mitosis found for each clone. The right panel shows the distribution of mitotic aberrations found for each stable Aurora-A type. Only the three main abnormal mitotic phenotypes observed, monopolar spindles, multipolar spindles, and cytokinesis failure, were quantified. The bars show data obtained for the three different clones of each variant and pooled into a single value.