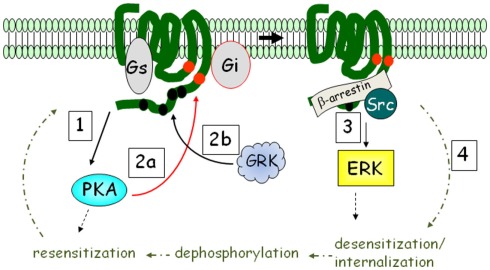
Figure 2.
βARs activate ERK MAPK in addition to PKA: the β2AR mechanism as an example. Upon catecholamine activation, PKA is activated (step 1), and phosphorylates the receptor at intracellular sites (red circles; step 2a). The receptor is also phosphorylated by G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) at multiple sites in the C-terminus (step 2b). PKA phosphorylation interdicts interaction with Gs to favor Gi, while GRK recruits β-arrestin, promoting ERK activation (step 3). β2AR is subject to rapid desensitization and internalization (step 4), whereupon phosphatases remove the phosphates and the receptor is recycled back to the plasma membrane.