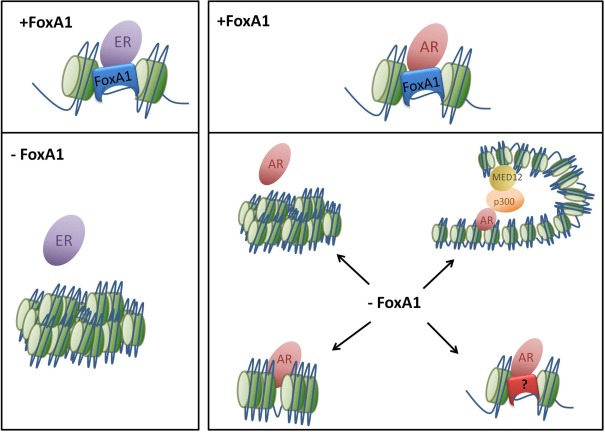
Figure 1.
Loss of FoxA1 has disparate effects on nuclear receptor binding. FoxA1 acts as a pioneer factor for ER and AR allowing the nuclear receptors to make targeted contacts with specific genomic regions which induce a transcriptional response. The loss of FoxA1 results in condensation of the chromatin so ER and AR can no longer bind to DNA at specific locations. However AR still appears to be able to bind in an unorthodox manner, without nucleosome redistribution or active histone marks. This may be due to changes in chromatin architecture and the development of new loops or through an alternate transcription factor.