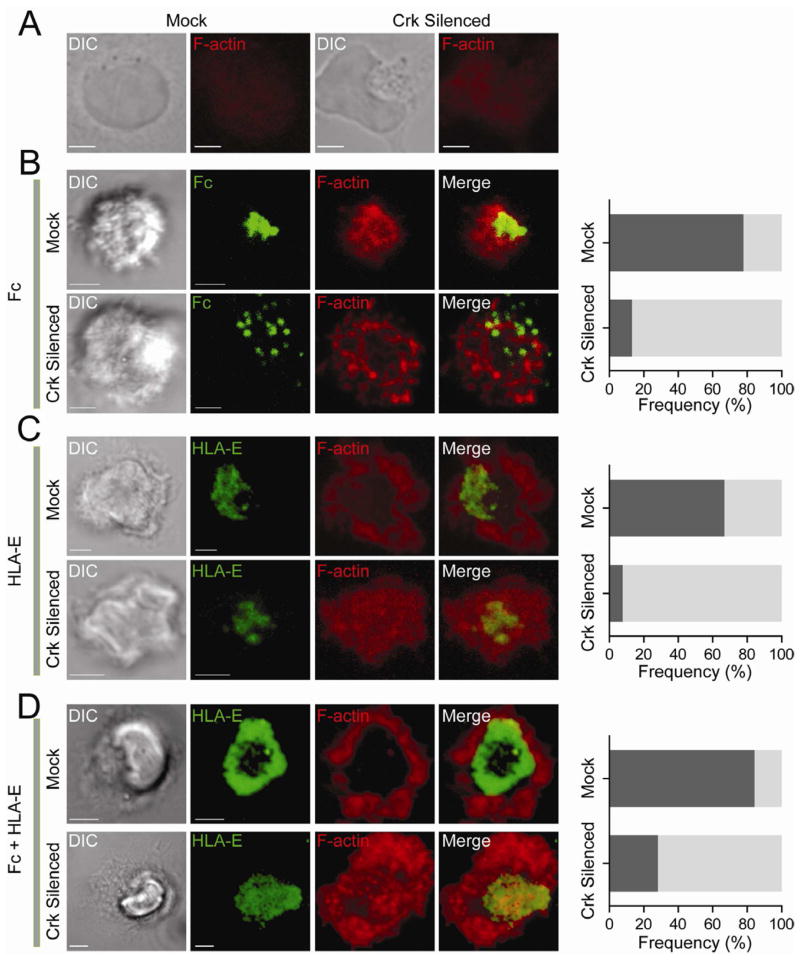
Figure 7. Crk Is Required for the HLA-E–Dependent Block in F-Actin Accumulation.
Confocal z-series of NK cells transfected with control siRNA (Mock) and Crk siRNAs (Crk silenced) and stained for F-actin with phalloidin-Alexa Fluor 647. Total CrkL was stained with primary Ab followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary Ab in order to select cells with strong silencing. DIC images are shown on the Left. Scale bars are 3.0 μm. (A) NK cells on poly-L-lysine. (B) NK cells incubated for ~60 min on lipid bilayers carrying Fc-Alexa Fluor 568. Dark shaded bars represent the frequency of cells with F-actin accumulation toward the center. Light shaded bars represent cells with disorganized or dispersed F-actin. (C) NK cells incubated for ~60 min on lipid bilayers carrying HLA-E-Alexa Fluor 568. Dark shaded bars represent cells with a peripheral F-actin ring. Light shaded bars represent cells with diffuse F-actin. (D) NK cells incubated for ~60 min on lipid bilayers carrying HLA-E-Alexa Fluor 568 and Fc. Dark shaded bars represent cells with a peripheral F-actin ring. Light shaded bars represent cells with disorganized F-actin. The images are representative of at least 20 cells in three independent experiments.