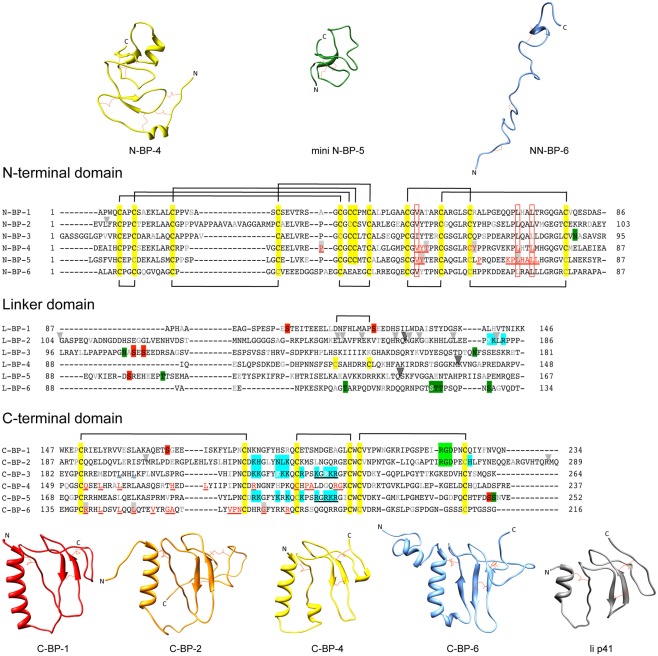
Figure 1.
Sequences and structures of IGFBP domains. Sequence alignments of IGFBP-1 to-6 N-terminal (N-), linker (L-), and C-terminal (C-) domains, highlighting cysteine residues (yellow box) and the disulfide bonding connectivity (black lines above and below sequences). Residue numbers are shown next to the sequences and every 10th residues is gray or white. The following distinctive features are highlighted: Red underlined text highlights IGF binding residues defined in structural studies of the N-domain [IGFBP-4 (Sitar et al., 2006) and mini IGFBP-5 (Kalus et al., 1998)] and C-domain [IGFBP-4 (Sitar et al., 2006) and IGFBP-6 (Headey et al., 2004a)]. Open red boxes, key residues involved in binding conserved across all IGFBPs; Light gray arrowheads, IGFBP-2 proteolysis sites (Ho and Baxter, 1997; Rehault et al., 2001; Monget et al., 2003; Standker et al., 2003; Mark et al., 2005; Berg et al., 2007; Miyamoto et al., 2007); Dark gray arrowhead, PAPP-A cleavage sites on IGFBP-2, -4, and -5 (Conover et al., 1995; Laursen et al., 2001; Monget et al., 2003); Blue boxes, IGFBP heparin-binding domains confirmed by site-directed mutagenesis or NMR-IGFBP-2 (Russo et al., 2005; Kuang et al., 2006), IGFBP-3 (Firth et al., 1998), and IGFBP-5 (Arai et al., 1996b); Filled red boxes, phosphorylation sites (Jones et al., 1993a; Coverley et al., 2000; Gibson et al., 2001; Graham et al., 2007; Dolcini et al., 2009); Light green boxes, integrin binding sites (Jones et al., 1993c; Kuang et al., 2006), Dark green boxes; glycosylation sites (Neumann et al., 1998; Firth and Baxter, 1999; Graham et al., 2007); Black underlined text, nuclear localization sequences (Schedlich et al., 1998; Iosef et al., 2008); Blue underlined text, Leu194 and Leu197 of IGFBP-3 involved in nuclear export (Paharkova-Vatchkova and Lee, 2010). Protein sequence SwissProt accession numbers are as follows: IGFBP-1 (P08833), IGFBP-2 (P18065), IGFBP-3 (P17936), IGFBP-4 (P22692), IGFBP-5 (P24593), IGFBP-6 (P24592). N-domain and C-domain ribbon structures are from the following database files: N-BP-4 (PDB 2DSR), mini N-BP-5 (PDB 1BOE, conformer 1), NN-BP-6 (PDB 2JM2), C-BP-1 (PDB 1ZT3), C-BP-2 (PDB 2H7T), C-BP-4 (PDB 2DSR), C-BP-6 (PDB 1RMJ), and the Ii p41 thryglobulin type 1 domain (PDB 1ICF). Some of these structures are derived from IGF:IGFBP complexes (see Table 1). For those NMR PDB files containing more than one conformer the first entry was used in this figure. Molecular graphic images were produced using UCSF Chimera program from Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California at San Francisco (http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera; Pettersen et al., 2004).