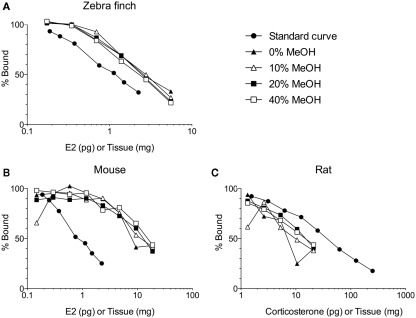
Figure 1.
Solid phase extraction of steroids from increasing amounts of brain tissue per assay tube. Samples were loaded onto C18 columns and washed with 10 ml of 0, 10, 20, or 40% methanol (MeOH) in water. Steroids were then eluted from the C18 columns with 5 ml of 90% MeOH. (A) The different washes have no effect on measurement of 17β-estradiol (E2) in zebra finch brain (Taves and Soma, unpublished data). (B) The different washes do affect measurement of E2 in mouse brain (Taves and Soma, unpublished data). (C) The different washes also affect measurement of corticosterone in rat brain (adapted with permission from Brummelte et al., 2010). The methods for all validations are similar (see Newman et al., 2008a). Briefly, brain tissue was homogenized in deionized water, and then MeOH was added. The samples were mixed and then left overnight at 4°C. The samples were mixed again and centrifuged (3000 g, 10 min, 2°C). Supernatants (≤1 ml) were diluted with 10 ml deionized water and loaded onto C18 columns (500 mg C18, non-endcapped). Prior to sample loading, the C18 columns were primed with 3 ml ethanol and equilibrated with 10 ml deionized water. After sample loading, columns were washed with 0, 10, 20, or 40% MeOH (10 ml) and steroids were eluted with 5 ml 90% MeOH. Eluates were dried in a vacuum centrifuge and resuspended in assay buffer. All reagents were HPLC-grade. E2 was measured using an ultrasensitive and specific radioimmunoassay (Beckman, DSL-4800; Charlier et al., 2010), and corticosterone was also measured using a radioimmunoassay (MP Biomedicals, cat. 07120103, Washburn et al., 2002).