Figure 7.
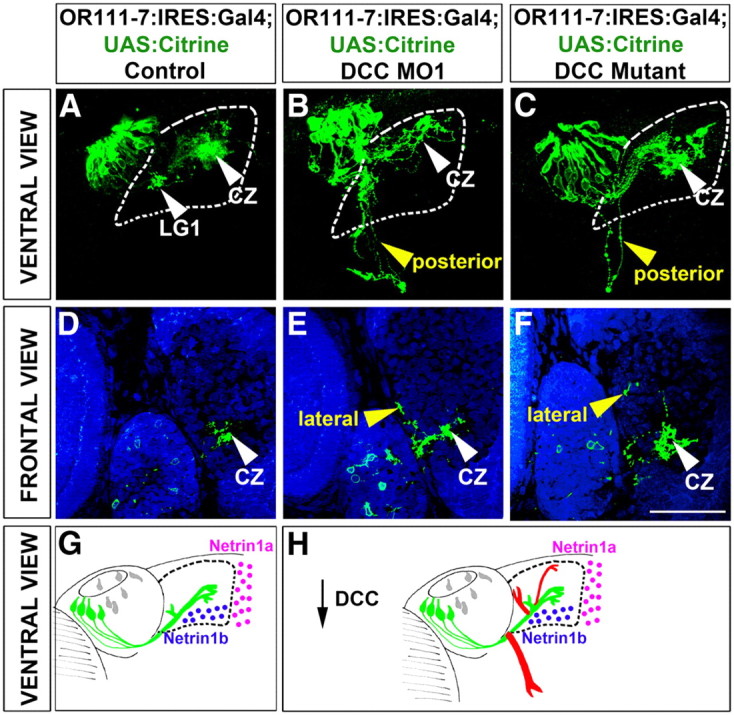
DCC signaling helps OR111-7 transgene-expressing axons enter the olfactory bulb and prevents non-protoglomerular mistargeting within the bulb. A–C, Maximum intensity projections of serial confocal optical sections of 3-d-old larvae (ventral view). Anterior is toward the top and the midline to the right of the image. The olfactory bulb is outlined with dashed lines. G, H, Schematics showing control OR111-7:IRES:Gal4; UAS:Citrine projections (green) and mistargeted axons (red) observed upon inhibiting DCC. The thickness of the red lines corresponds roughly to the penetrance of the indicated phenotypes. Netrin1a mRNA (pink dots) is expressed at the telencephalic midline and netrin1b mRNA (blue dots) is expressed in the ventral bulb. A, G, OR111-7 transgene-expressing axons (green) primarily target the central zone (CZ, white arrowhead) and LG1. B, C, H, In DCC MO1 morphants and in the DCC mutant, some OR111-7 transgene-expressing axons extend posteriorly away from the olfactory bulb and do not enter it (posterior, yellow arrowhead). D–F, Single confocal optical sections through frontally mounted 3-d-old OR111-7:IRES:Gal4; UAS:Citrine larvae. Propidium iodide (blue) delineates distinct protoglomeruli in the olfactory bulb. D, OR111-7:IRES:Gal4; UAS:Citrine axons are detected in the central zone (CZ, white arrowhead). E, F, Reducing DCC levels via DCC MO1 morpholino or in the hypomorphic DCC mutant causes some OR111-7-transgenic axons to mistarget toward the lateral border of the olfactory bulb posterior to the LG1 protoglomerulus (lateral, yellow arrowhead, schematized in Fig. 3M,N). Scale bar (in F): A–F, 50 μm.
