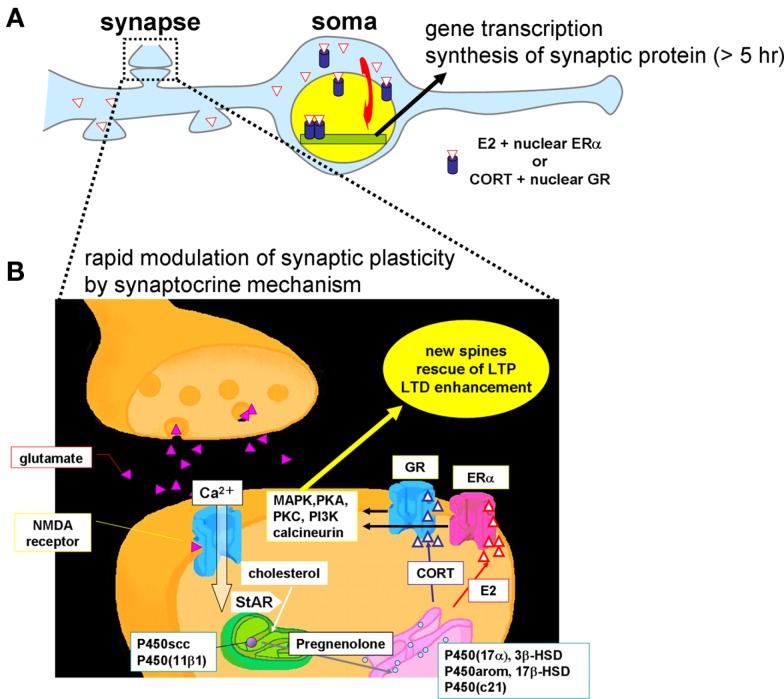
Figure 11.
Schematic illustration of synaptic actions by hippocampus-synthesized steroids. (A) Slow modulation of synaptic plasticity via gene transcription and synthesis of synaptic proteins in neurons. The delayed action of E2 or CORT is mediated by ERα/ERβ or GR in cytoplasm and nuclei, respectively. New synaptic connections are formed by synthesized synaptic proteins or neurotrophic factors. (B) Rapid modulation of the synaptic plasticity via synaptic ERα and GR. Hippocampal neurons synthesize much higher level of E2 than that from circulation. The level of hippocampus-synthesized CORT is in the order of 10 nM which is sufficient to increase density of dendritic spines. Upon Ca2+ influx via NMDA receptor, transport of cholesterol to inner membrane of mitochondria by StAR is facilitated, resulting in enhancement of steroid synthesis. P450scc and P450 (11β1) are localized in mitochondria and P450 (17α), 3β-HSD, P450arom, 17β-HSD, and P450 (c21) are localized in endoplasmic reticulum. Hippocampus-synthesized sex steroids and corticosteroids bind to synaptic ERα and GR which drive signal cascades mediated via various kinases and phosphatases.