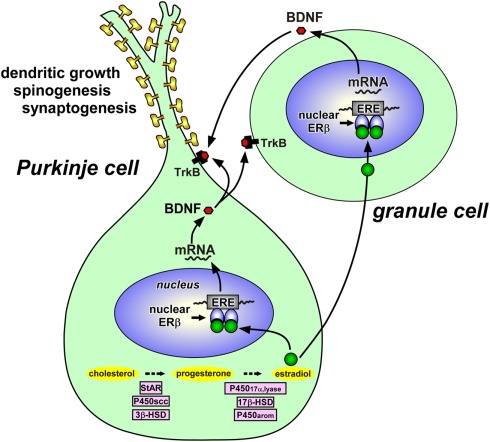
Figure 3.
Schematic model depicting possible actions of estradiol in the Purkinje cell during development. Estradiol acts on the Purkinje cell through intranuclear receptor (ERβ)-mediated mechanisms that promote dendritic growth, spinogenesis, and synaptogenesis in this neuron by genomic mechanisms. Both Purkinje cells and granule cells express BDNF and TrkB, a receptor for BDNF. Estradiol induces the expression of BDNF, which may act on Purkinje cells and granule cells through TrkB-mediated mechanisms to promote Purkinje dendritic growth, spinogenesis, and synaptogenesis. See the text for details. StAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory protein; P450scc, cytochrome P450 side-chain cleavage enzyme; 3β-HSD, 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ5-Δ4-isomerase; P45017α,lyase, cytochrome P450 17α-hydroxylase/c17,20-lyase; 17β-HSD, 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; P450arom, cytochrome P450 aromatase; ERβ, estrogen receptor-β; ERE, estrogen response element; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; TrkB, BDNF receptor.