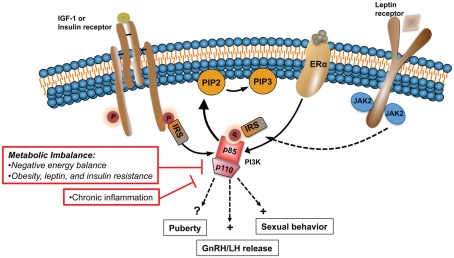
Figure 2.
States of metabolic imbalance such as malnutrition and obesity have detrimental effects on the HPG axis, principally altering normal GnRH pulsatile release. Alterations in the levels and sensitivity to peripheral hormones and metabolic signals, including IGF-1, E2, leptin, and insulin, play a major role in the dysfunction of the HPG axis during chronic metabolic disturbances. PI3K is a major signaling pathway activated by the same upstream regulators that are affected during such states. In rodents, PI3K participates in the central control of sexual behavior and LH release. In this model altered PI3K signaling is linked to the negative effects that metabolic imbalance has on the HPG axis.