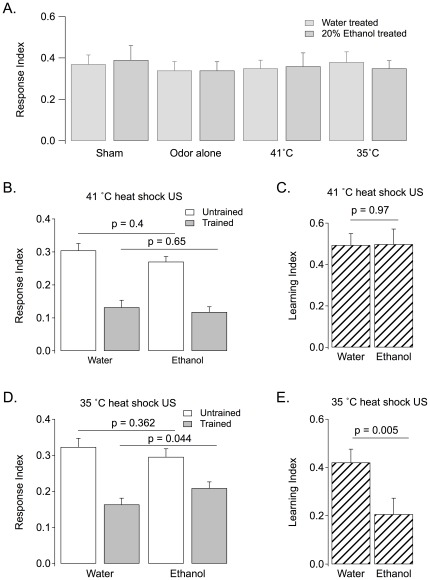
Figure 4. Ethanol treatment affects olfactory learning when the heat shock unconditioned stimulus is below the temperature optima.
A. Either heat alone or odor alone presentations resulted in the same response index (RI = #Larvae in odor zone/#Larvae total) as sham-treated larvae (p>0.05 for any comparison). B. Response indices for untrained (control) and trained larvae are shown for animals that either received water or 20% EtOH. All larvae were trained to associate the odor with a 41°C heat-shock. The response indices were similar for water-treated and ethanol-treated groups when comparisons were made for similar conditions such as the untrained group or the trained group. C. Learning indices (LI = (RIcontrol−RIconditioned)/RIcontrol) calculated from the data in Panel B. D. Response indices for untrained (control) and trained larvae are shown for animals that either received water or 20% EtOH. All larvae were trained to associate the odor with a 35°C heat-shock. The conditioned response indices are significantly different in the ethanol treated groups (n = 32; p = 0.044). E. Learning indices calculated from the data in Panel D. Ethanol induced a significant reduction in learning.