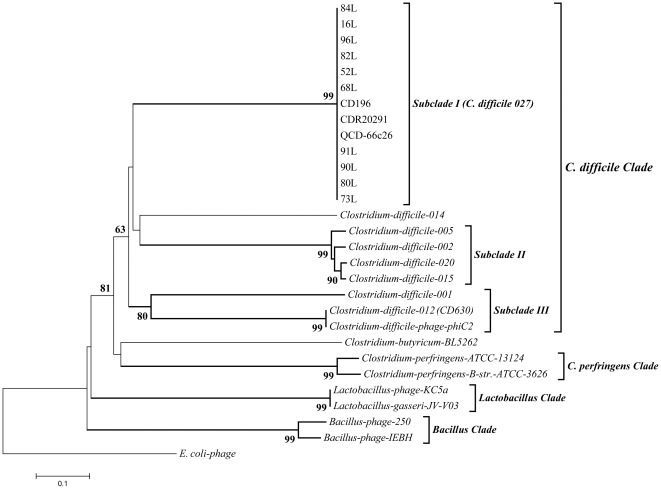
Figure 3. Evolutionary relationship of Clostridium difficile based on the myovirus capsid gene.
The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) is shown next to the branches. The evolutionary distances were computed using the p-distance method based on their amino acid sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. The analysis involved 29 amino acid sequences of 10 (84L, 16L, 96L, 82L, 52L, 68L, 91L, 90L, 80L and 73L) representative isolates of the ribotype 027 subclades and seven other ribotypes (ribotypes 014, 005, 002, 020, 015 and 001). Five other sequences including CD196, CDR20291 and QCD-66c26 (ribotype 027), CD630 (ribotype 012) and phiC2 were obtained from in-silico PCR. Other sequences were obtained from NCBI searches. All sequences with 75% similarities were assigned into a subclade. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA5.