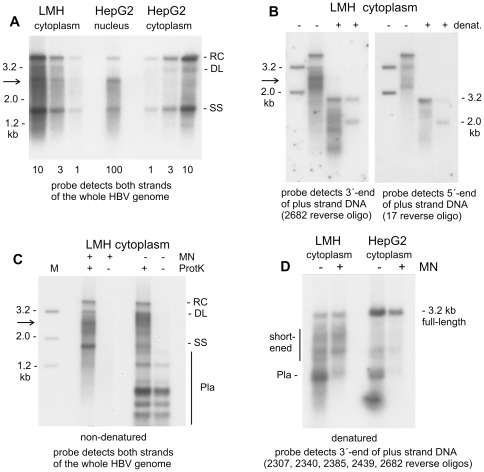
Figure 3. Detection of shortened HBV genomes in the cytoplasm of LMH cells.
Transfection was done with a plasmid coding for splice-deficient virus with the natural HBV core promoter driving transcription of pgRNA and the surface protein coding sequence mutated. (A) Viral DNA from cytoplasm of LMH cells was compared with viral DNA from HepG2 cell nuclei and HepG2 cytoplasm. Preparation of viral DNA involved nuclease treatment of cytoplasmic lysates and purified cell nuclei. Numbers below indicate relative amounts of DNA loaded in the respective lanes. Hybridisation was done with a probe encompassing both strands of the whole HBV genome. The arrow points to a prominent DNA species obtained both in cytoplasm of LMH cells and nucleus of HepG2 cells. (B) Viral DNA from transfected LMH cells was denatured (+/− denat) by heating before gel loading, as indicated. Hybridisation was done with 32P-labelled oligonucleotides detecting either the 3′-end or the 5′-end of plus-strand DNA at genome positions 2682 and 17 (see map of the HBV genome in Figure 1D). Positions of the 3.2 kb and 2.0 kb marker fragments are indicated. The arrow points to viral genomes migrating between these marker fragments. (C) Viral DNA was prepared from cytoplasm of transfected LMH cells with or without micrococcal nuclease (+/− MN) treatment and with or without protease (+/− ProtK) digestion done before phenol extraction. The purified DNA was digested with restriction enzyme DpnI, which selectively cuts transfected plasmid (Pla) into multiple short fragments. Southern blot hybridisation was done with a probe covering both strands of the whole HBV genome. This probe also detects several DpnI fragments of transfected plasmid DNA. (D) Viral DNA was prepared from cytoplasm of HepG2 and LMH cells with or without micrococcal nuclease (+/− MN) treatment. Purified DNA was subsequently digested with restriction enzyme DpnI and denatured by heating before gel electrophoresis. Southern blot hybridisation was done with a mixture of 32P-labeled oligonucleotide complementary to the 3′-end of plus-strand DNA at genome position 2307, 2340, 2385, 2439 and 2682. These five oligonucleotides were combined to enhance sensitivity. The vertical lane on the right side indicates shortened plus-strand molecules. The probe detects a 0.8 kb DpnI fragment of the transfected plasmid (Pla) if micrococcal nuclease treatment is not done.