Table 2. Sampling and grazing beating statistics.
| no prey | S. major | Karenia brevis | Karlodinium veneficum | |||||||
| SP-1 (non-toxic) | 2228 (toxic) | 2228+S.major | 1609 (non-toxic) | 2064 (toxic) | 2064+1609 | |||||
| 1∶3 | 3∶1 | 1∶3 | 3∶1 | |||||||
| Cell concentration(cell/ml) | N/A | 2039 | 1855 | 3373 | 2728 | 1844 | 1776 | 2414 | 2004 | 1723 |
| Sampling beating fraction★ | 0.022 | 0.039 | 0.052 | 0.053 | 0.036 | 0.024 | 0.059 | 0.069 | 0.049 | 0.049 |
| Grazing beating fraction★ | 0.000 | 0.281 | 0.209 | 0.082 | 0.042 | 0.010 | 0.118 | 0.073 | 0.174 | 0.109 |
| Corr. sampling fraction♦ | N/A | 0.036 | 0.044 | 0.081 | 0.045 | 0.021 | 0.048 | 0.076 | 0.044 | 0.038 |
| Corr. grazing fraction♦ | N/A | 0.302 | 0.248 | 0.053 | 0.034 | 0.011 | 0.146 | 0.066 | 0.190 | 0.139 |
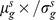 (ms)• (ms)•
|
54×/1.88 | 75×/2.19 | 61×/1.95 | 65×/1.75 | 69×/1.98 | 52×/1.80 | 56×/2.07 | 61×/1.78 | 71×/1.94 | 69×/2.22 |
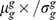 (ms)• (ms)•
|
N/A | 347×/1.66 | 235×/1.88 | 258×/1.51 | 342×/1.54 | 169×/4.97 | 275×/1.91 | 264×/1.48 | 254×/1.64 | 245×/1.51 |
| rms fitting error – grazing◊ | N/A | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.90 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
The total duration of sampling/grazing divided by the observation time.
Values corrected for differences in prey cell concentration.
For a normally-distributed variable, a domain consisting of ± standard deviation from the arithmetic mean contains 68.3% of the data. For a log-normally-distributed variable, 68.3% of the results fall within the range of the geometric mean ×/(multiply/divide) by the geometric standard deviation. Accordingly, 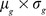 represents a confidence interval of 68.3% [38].
represents a confidence interval of 68.3% [38].
errors resulting from log-normal fits.
