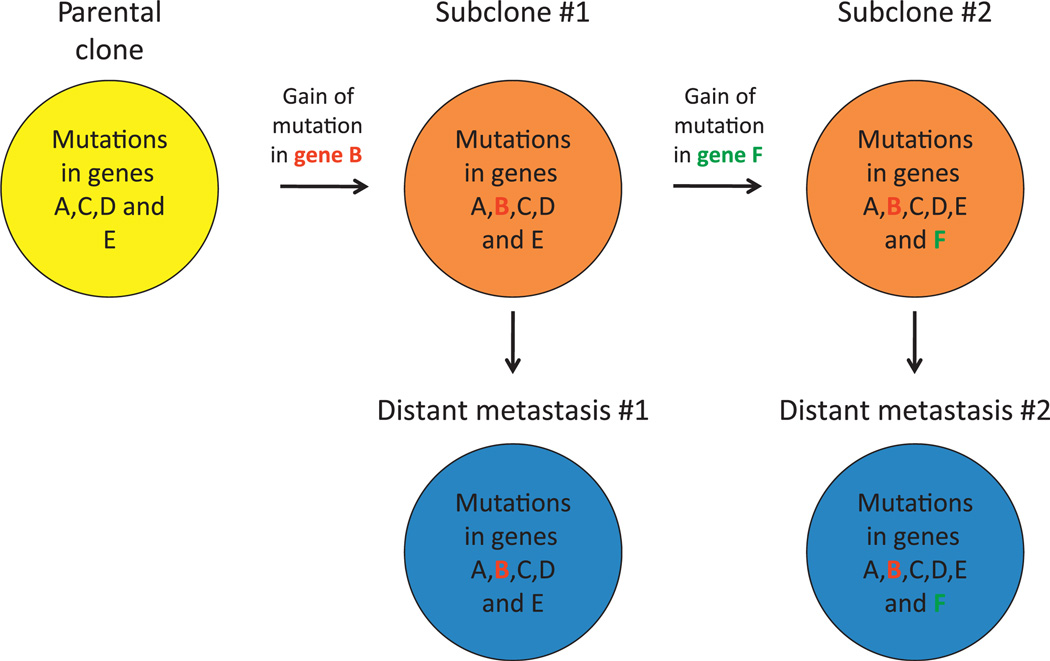
Figure 5.
Clonal progression of pancreatic cancer. A representative example of the proposed clonal evolution of pancreatic cancer based on sequencing data of five different samples is shown. In this model, after development of the parental clone that seeded the infiltrating carcinoma (indicated in yellow), ongoing clonal evolution continues within the primary carcinoma leading to the development of a subclone characterised by the gain of a mutation in gene B. Additional clonal evolution beyond this subclone leads to the development of a second subclone characterised by the presence of a mutation in gene F. Subclones may then seed metastases to distant sites (indicated in blue) as reflected by the identical pattern of mutations in subclone 1 compared with distant metastasis 1, and in subclone 2 compared with distant metastasis 2.